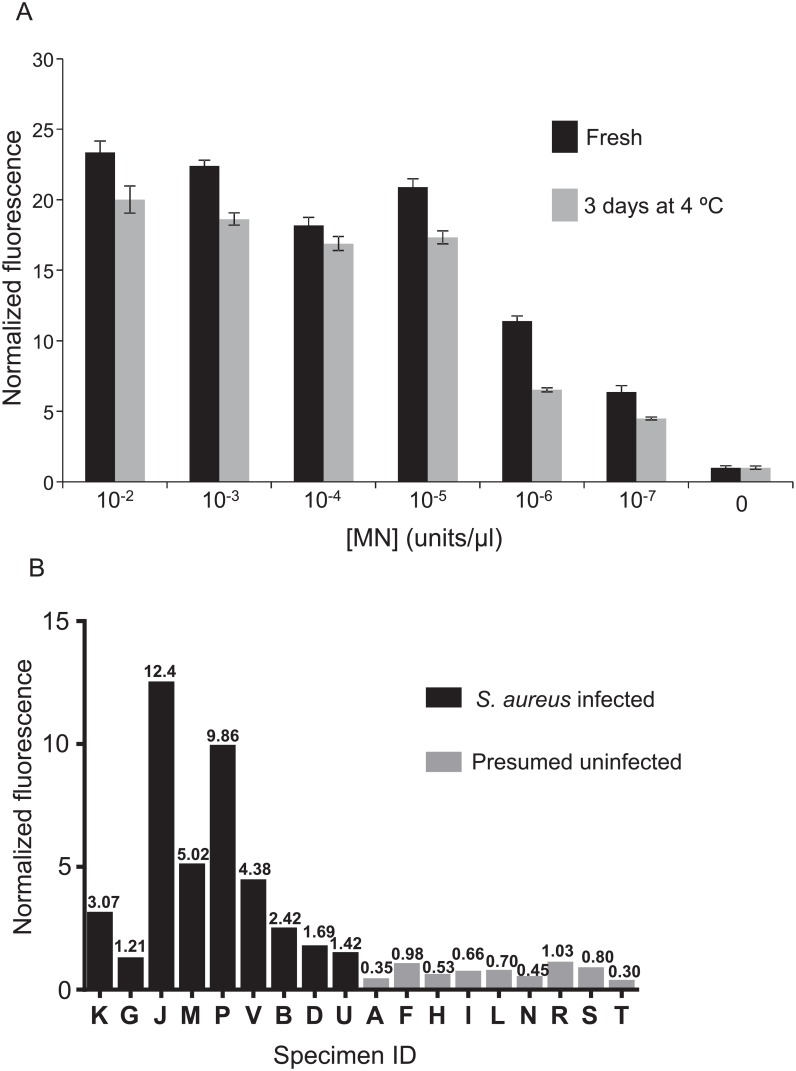
Fig 3. Detection of MN in SAB patient plasma.
First, the stability of MN in human plasma at 4°C was determined by spiking pooled human plasma with the indicated concentrations of MN and storing at 4°C for 3 days, followed by MN activity measurement (A). Equivalent amounts of MN were also added to pooled human plasma immediately before the nuclease assay for comparison. For the assay, calcium chloride was added to all samples, which were then heated to denature inhibitory antibodies. Supernatants of heated plasma samples were incubated with the 11mer PolyT FAM probe for 1 hour and fluorescence was measured with a plate-reader. All values are normalized to those produced by control samples in which nuclease was omitted. Error bars indicate standard deviations of triplicate measurements. In part B, MN activity assays were carried out with plasma specimens from S. aureus bacteremic (S. aureus infected) and individuals showing no signs of active infections (Presumed uninfected). 660 μl of plasma was used for each and the 11mer PolyT FAM probe was used for detection. Fluorescence values were normalized to those of control samples in which buffer was substituted for plasma; note normalization values included above each bar. Data shown are compiled from several independent experiments.