Figure 1.
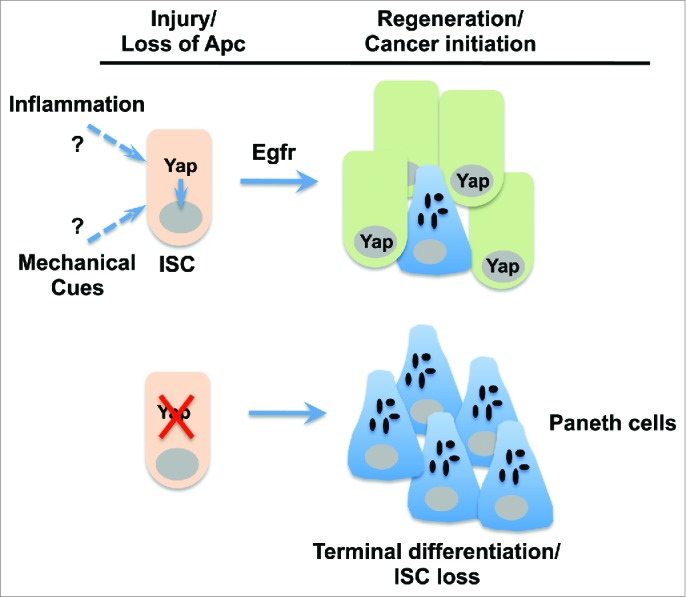
Functions of Yap in intestinal stem cells during tissue regeneration and tumorigenesis. Upon injury or loss of the tumor suppressor Apc (adenomatous polyposis coli), Yap (Yes-associated protein) promotes epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) signaling and maintains proper coupling of intestinal stem cell (ISC) self renewal and Paneth cell differentiation. In the absence of Yap, ISCs preferentially differentiate into Paneth cells and are ultimately lost. The precise signal leading to Yap nuclear activation is unknown but may involve inflammatory cytokines and/or mechanical stress imposed on ISCs as a result of tissue damage.
