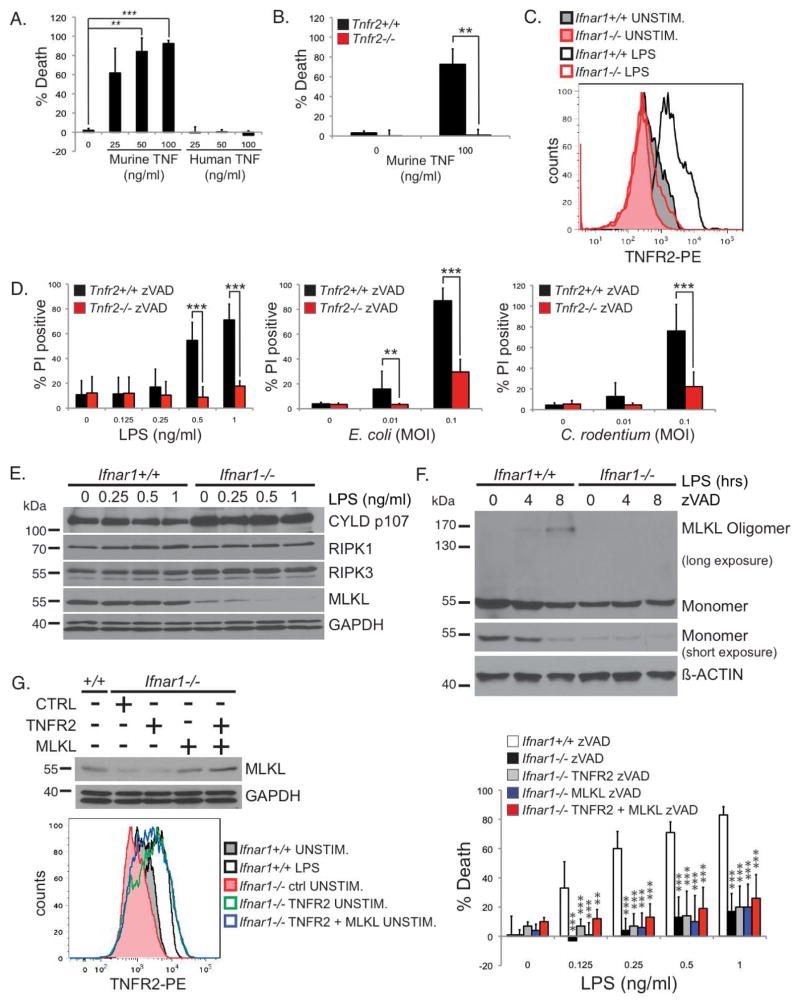
FIGURE 6. Type I IFN licenses TNF-mediated necroptosis by inducing TNFR2 and MLKL expression.
(A) Wild type BMDMs were stimulated with indicated amounts of murine or human TNF for 24 hours in the presence of zVAD-fmk. (B) Tnfr2+/+ and Tnfr2−/− BMDMs were stimulated with murine TNF for 24 hours in the presence of zVAD-fmk. (A, B) Viability was determined by CellTiter-Glo assays as in Figure 3C. (C) Ifnar1+/+ and Ifnar1−/− BMDMs stimulated with 1 ng/ml of LPS for 24 hours were stained with a PE-conjugated anti-TNFR2. Data is representative of three independent experiments. (D) Necroptosis in Tnfr2+/+ and Tnfr2−/− BMDMs were analyzed as in Figure 3A & B. (E) Ifnar1+/+ or Ifnar1−/− BMDMs were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of LPS for 4 hours. Triton-soluble lysates were blotted with antibodies for CYLD (D1A10), RIPK1, RIPK3, MLKL, and GAPDH. (F) Ifnar1+/+ or Ifnar1−/− BMDMs were pre-treated with 25 μM zVAD-fmk and stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for the indicated times. MLKL oligomerization was analyzed as in Figure 4C. Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. (G) Ifnar1−/− BMDMs were transduced with retroviruses encoding a control protein, TNFR2, or MLKL, as indicated. Lysates from these cells were blotted to confirm MLKL expression. Ifnar1−/− BMDMs transduced with TNFR2 or MLKL were stained with PE-conjugated anti-TNFR2 to confirm TNFR2 expression that is equivalent to that of Ifnar1+/+ BMDMs stimulated with 10 ng/ml of LPS for 24 hours. These cells were stimulated with LPS in the presence of 25uM of zVAD-fmk. Viability was determined by CellTiter-Glo as in Figure 3C.