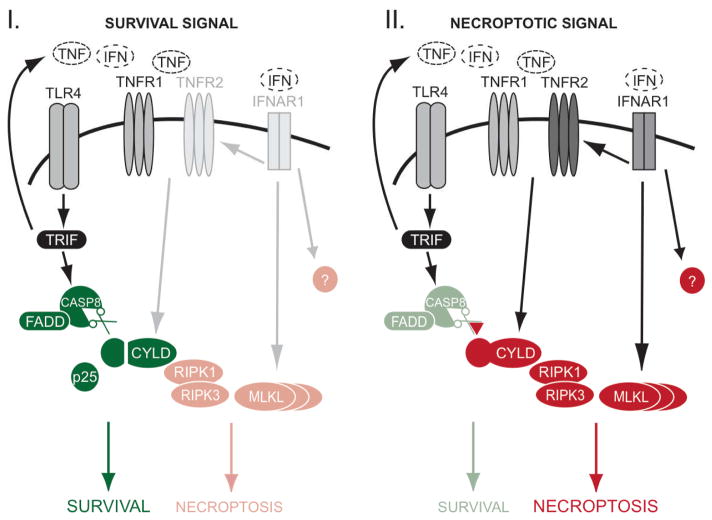
FIGURE 7. Regulation of survival and necroptosis in macrophages.
During an infection, the determination of TNF-induced necroptosis is subject to cross-regulation by other receptor pathways. I: TLR4 activates CASPASE-8 through a TRIF-dependent manner to proteolyze and remove CYLD. CYLD is essential for TNF-induced necroptosis, and so its removal prevents macrophages from undergoing necroptosis that can be induced by the TNF produced during bacterial infection. II: Inhibition of CASPASE-8 stabilizes CYLD and this results in necroptosis mediated by auto-produced TNF signaling via CYLD. Type I IFN plays a licensing role because it is required for the induction of TNFR2, MLKL and other uncharacterized molecules that are essential for TNF-mediated necroptosis.