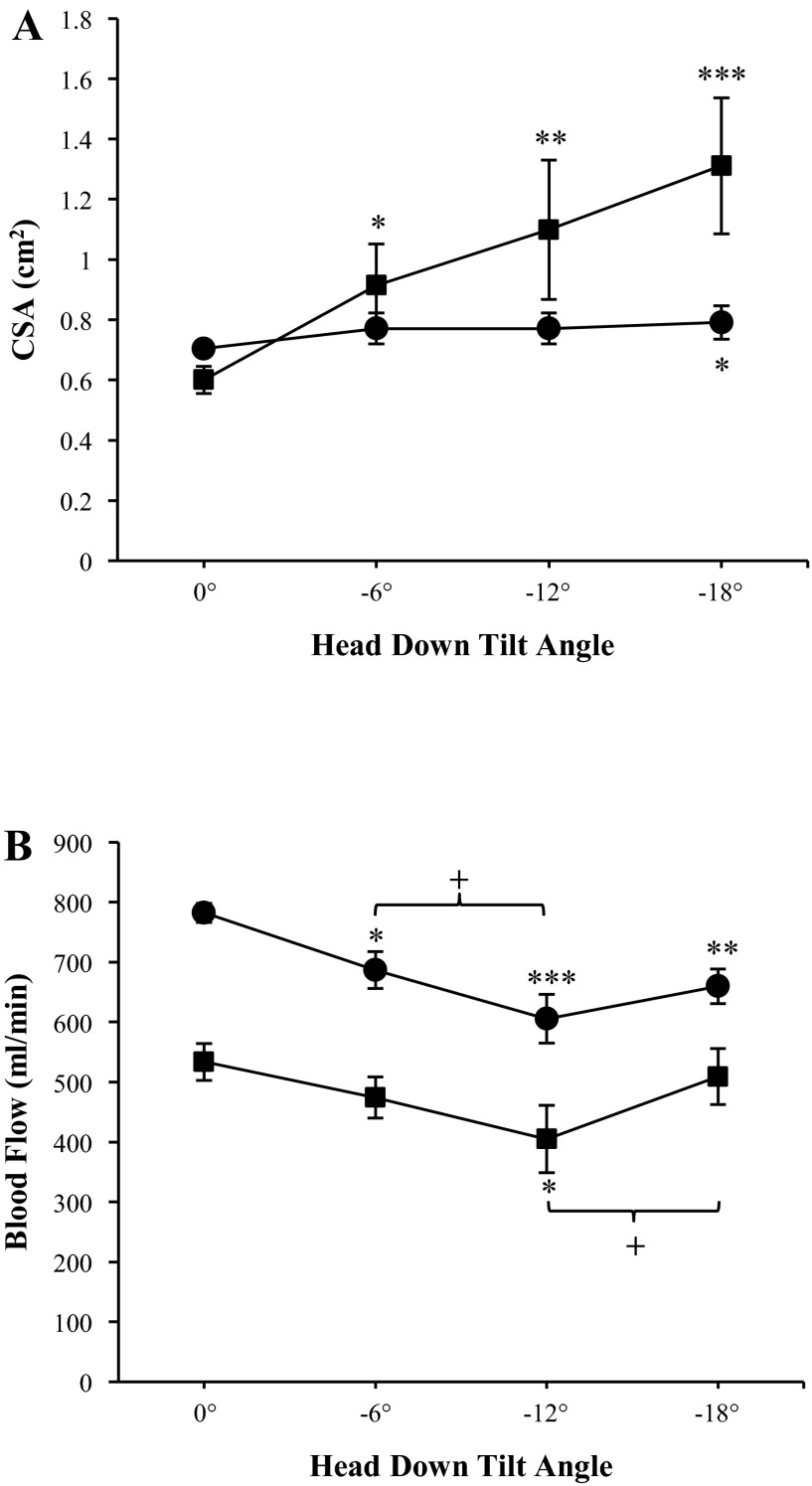
Fig. 2.
Effects of different head-down tilt angles on total cross-sectional area (CSA; A) and total flow (B) for the arterial (●) and internal jugular venous (■) systems. Measurements were taken at baseline (0°) and after 4.5-h head-down tilt at various angles with phase-contrast MRI. Flow was calculated by multiplying blood flow velocity by the CSA for each vessel. Blood flow through the bilateral internal carotid and vertebral arteries were summed to give total arterial inflow, and blood flow through the bilateral internal jugular veins were summed to give jugular venous outflow. Values are means ± SE. *P <0.05. **P <0.01. ***P <0.001. +P <0.05.