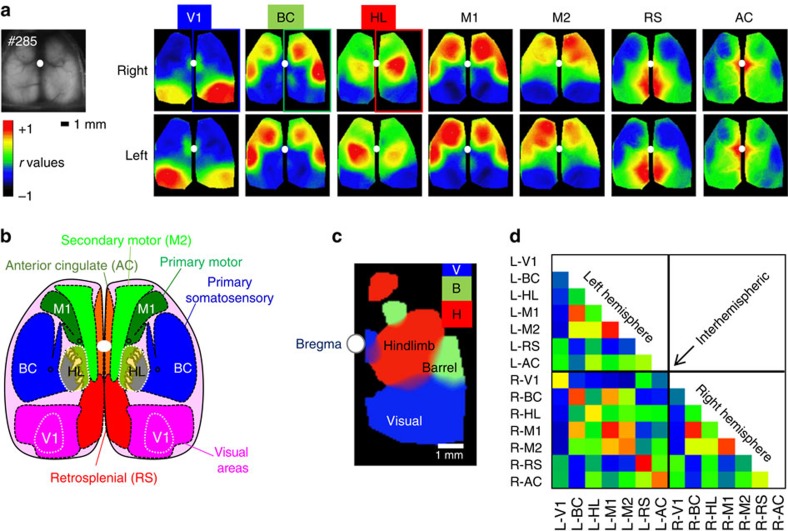
Figure 6. High specificity of functional connectivity mapping using resting-state spontaneous activity for mice with extended head-fixed imaging.
(a) Spontaneous and drinking-evoked activity was collected during the extended head-fixation of GCaMP6s mouse #0285 from cage GU (total immobilized time of 1,064 s). Basal green fluorescence and correlation maps for seed pixel located in right (upper maps) and left (lower maps) V1, BC, HL, M1, M2, RS and AC. (b) Atlas of the dorsal region of the cortex (adapted from the Allen Mouse Brain Connectivity Atlas), much of barrel cortex is likely off the craniotomy. (c) Composite thresholded map of the high correlation region showing the remote ipsilateral connectivity for seed pixel in V (blue, visual), B (green, barrel cortex) and H (red, hindlimb). Islands of remote co-activation are present in the motor cortex for HL and BC seeds (smaller red and green blobs, respectively), while V1 seeds show remote activity in AC near the white dot marking bregma. (d) Matrix of correlation between regions presented in a. No correction for intra-trial movement was necessary in these data sets. The window was installed 25 days before acquisition.