Table 3. The optical constants of 2D MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2 with different excitation wavelengths from 600 nm to 1024 nm.
| TMDC | TMX2 (nm) | λ = 600 nm | λ = 633 nm | λ = 660 nm | λ = 785 nm | λ = 1024 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2 | 0.65 | ɛ′ = 17.7967, | ɛ′ = 24.4368, | ɛ′ = 23.4129, | ɛ′ = 21.4675, | ɛ′ = 20.8372, |
| ɛ″ = 10.7801 | ɛ″ = 11.9121 | ɛ″ = 12.5610 | ɛ″ = 1.0781 | ɛ″ = 0.9662 | ||
| MoSe2 | 0.70 | ɛ′ = 21.3204, | ɛ′ = 20.3560, | ɛ′ = 19.3366, | ɛ′ = 17.7994, | ɛ′ = 14.9028, |
| ɛ″ = 10.9486 | ɛ″ = 9.3039 | ɛ″ = 8.4366 | ɛ″ = 7.0709 | ɛ″ = 2.7611, | ||
| WS2 | 0.80 | ɛ′ = 12.0258, | ɛ′ = 23.8511, | ɛ′ = 19.9701, | ɛ′ = 16.0968, | ɛ′ = 25.0445, |
| ɛ″ = 4.2578 | ɛ″ = 3.0578 | ɛ″ = 1.8420 | ɛ″ = 0.3203 | ɛ″ = 2.5676, | ||
| WSe2 | 0.70 | ɛ′ = 19.4125, | ɛ′ = 20.5156, | ɛ′ = 18.7344, | ɛ′ = 19.0563, | ɛ′ = 23.6474, |
| ɛ″ = 8.4135 | ɛ″ = 3.9423 | ɛ″ = 2.1955 | ɛ″ = 0.3205 | ɛ″ = 2.3801 |
The dielectric constant is described by
ε = ε′ + ε″i,
where the real part ε′
relates to the stored energy within the medium and the
imaginary part ε″ relates to
the dissipation of energy within the medium. (The complex
refractive index 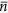 is defined
as
is defined
as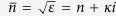 , where the real
part n indicates the phase velocity, while the
imaginary part κ known as the extinction
coefficient refers to the mass attenuation coefficient).
, where the real
part n indicates the phase velocity, while the
imaginary part κ known as the extinction
coefficient refers to the mass attenuation coefficient).
