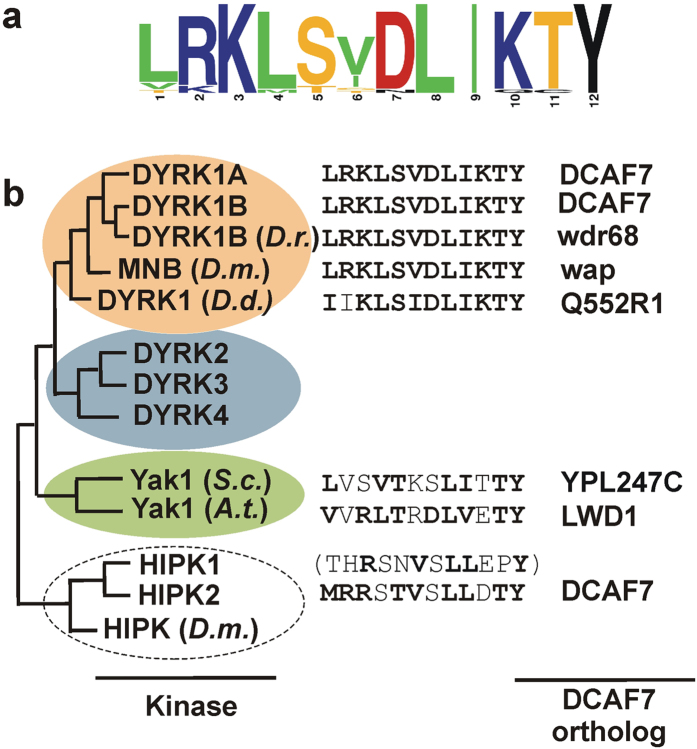
Figure 9. Evolutionary conservation of the DYRK/DCAF7 interaction.
(a) Consensus sequence of the DCAF7 binding motif in class 1 DYRKs. - The sequence logo was created from an alignment9 of 19 representative sequences of class 1 DYRKs in the animal kingdom, including sponges, jellyfish, sea urchin, insects and different worms using the WebLogo application52. (b) Phylogenetic relationship of the DYRKs and HIPKs that interact with DCAF7. – Conservation of the DCAF7 binding sequence is illustrated for kinases that are known to bind DCAF7 or orthologous proteins. Mammalian DYRK2-4 and HIPK1 do not bind DCAF7. It is unknown whether Drosophila HIPK binds to the wap protein, but the DCAF7 binding site from HIPK2 is not conserved in invertebrates. Kinase branches from top to bottom: class 1 DYRKs, class 2 DYRKs, YAK branch of DYRKs, HIPKs. Non-mammalian kinases are from Danio rerio (D.r.), Drosophila melanogaster (D.m.), Dictyostelium discoideum (D.d.), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.c.), and Arabidopsis thaliana (A.t.).