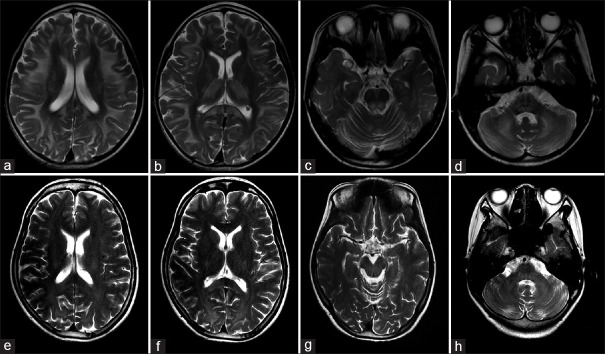
Figure 2.
Brain MRIs of two KSS patients. (a-d) Brain MRI in patient 2 showed abnormal high-T2 signals in the subcortical white matter with U-fibers involved (a), splenium of corpus callosum, internal capsule, basal ganglia, and thalamus (b), dorsal brainstem (c), and brachium pontis and cerebellar white matter (d), respectively. (e-h) Brain MRI in patient 6 showed abnormal high-T2 signal signals in the periventricular white matter (e), splenium of corpus callosum, internal capsule (f), dorsal brainstem (g), brachium pontis, and cerebellar white matter (h), respectively. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; KSS: Kearns-Sayre syndrome.