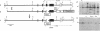Abstract
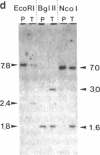
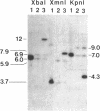
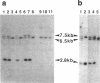
We have inactivated the endogenous apolipoprotein E (apoE) gene by using gene targeting in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. Two targeting plasmids were used, pJPB63 and pNMC109, both containing a neomycin-resistance gene that replaces a part of the apoE gene and disrupts its structure. ES cell colonies targeted after electroporation with plasmid pJPB63 were identified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) followed by genomic Southern analysis. Of 648 G418-resistant colonies analyzed, 9 gave a positive signal after PCR amplification, and 5 of them were confirmed as targeted by Southern blot analysis. The second plasmid, pNMC109, contains the negatively selectable thymidine kinase gene in addition to the neomycin-resistance gene. After electroporation with this plasmid, 177 colonies resistant both to G418 and ganciclovir were analyzed; 39 contained a disrupted apoE gene as determined by Southern blotting. Chimeric mice were generated by blastocyst injection with 6 of the targeted lines. One of the lines gave strong chimeras, three of which transmitted the disrupted apoE gene to their progeny. Mice homozygous for the disrupted gene were produced from the heterozygotes; they appear healthy, even though they have no apolipoprotein E in their plasma.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg K. Genetics of coronary heart disease. Prog Med Genet. 1983;5:35–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyles J. K., Zoellner C. D., Anderson L. J., Kosik L. M., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Hui D. Y., Mahley R. W., Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Ignatius M. J. A role for apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein A-I, and low density lipoprotein receptors in cholesterol transport during regeneration and remyelination of the rat sciatic nerve. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1015–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI113943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Apolipoprotein genetic variation and human disease. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jan;68(1):85–132. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus M. C., Chapman M. J., Forgez P., Laplaud P. M. Distribution and characterization of the serum lipoproteins and apoproteins in the mouse, Mus musculus. J Lipid Res. 1983 Sep;24(9):1210–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. The new mouse genetics: altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G., Zannis V. I. The molecular basis of a familial apoE deficiency. An acceptor splice site mutation in the third intron of the deficient apoE gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2310–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Getz G. S. Extrahepatic synthesis of apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1368–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Gascon P., Breser H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6795720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Rivera-Pérez J., Chang C., Bradley A. Target frequency and integration pattern for insertion and replacement vectors in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4509–4517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M., Hardy K., Handyside A., Hunter S., Monk M. HPRT-deficient (Lesch-Nyhan) mouse embryos derived from germline colonization by cultured cells. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):292–295. doi: 10.1038/326292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Tajima S., Menju M., Yamamoto A. Structure and expression of mouse apolipoprotein E gene. J Biochem. 1989 Jul;106(1):98–103. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Immunoregulatory plasma lipoproteins. Role of apoprotein E and apoprotein B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11775–11781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein binding to canine hepatic membranes. Metabolically distinct apo-E and apo-B,E receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5646–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Hagemann L. J., Doetschman T., Hagaman J. R., Huang S., Williams P. J., First N. L., Maeda N., Smithies O. Germ-line transmission of a planned alteration made in a hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8927–8931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Marrack P., Kappler J. W., Smithies O. Normal development of mice deficient in beta 2M, MHC class I proteins, and CD8+ T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1227–1230. doi: 10.1126/science.2112266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaka D., Teramoto T., Matsushima T., Yokoyama T., Yamada A., Aikawa T., Miyamoto Y., Kurokawa K. Apolipoprotein E deficiency with a depressed mRNA of normal size. Atherosclerosis. 1991 May;88(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc A. C., Poduslo J. F. Regulation of apolipoprotein E gene expression after injury of the rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Feb;25(2):162–171. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Itoh H., Takeda M., Kajinami K., Wakasugi T., Koizumi J., Takeda R., Asagami C. A young type III hyperlipoproteinemic patient associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Metabolism. 1989 Feb;38(2):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Angelin B. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: recent insights into the genetic defect of familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Adv Intern Med. 1984;29:385–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. The molecular basis of atherosclerosis: concepts derived from studies of lipoprotein metabolism and cell biology. Clin Invest Med. 1986 Nov;9(4):304–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Castle C. K., Goodman L. V., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Shooter E. M., Gebicke-Haerter P. J. Expression of apolipoprotein E by cultured vascular smooth muscle cells is controlled by growth state. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millis A. J., Hoyle M., Kent L. In vitro expression of a 38,000 dalton heparin-binding glycoprotein by morphologically differentiated smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jun;127(3):366–372. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Mitchell D., Reue K., Morrow A., Lusis A. J., LeBoeuf R. C. Ath-1, a gene determining atherosclerosis susceptibility and high density lipoprotein levels in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Kaptein J. S., Reue K. L., Lusis A. J. Evolution of apolipoprotein E: mouse sequence and evidence for an 11-nucleotide ancestral unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8085–8089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. H., Shesely E. G., Kim H. S., Smithies O. Cotransformation and gene targeting in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2769–2777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the sinusoidal transport process responsible for uptake of chylomicrons by the liver. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1859–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B. Heterogeneity of human plasma very low density lipoproteins. Separation of species differing in protein components. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):502–507. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Targeted disruption of the murine int-1 proto-oncogene resulting in severe abnormalities in midbrain and cerebellar development. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):847–850. doi: 10.1038/346847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware L. M., Axelrad A. A. Inherited resistance to N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro: evidence that congenic mouse strains SIM and SIM.R differ at the Fv-1 locus. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]