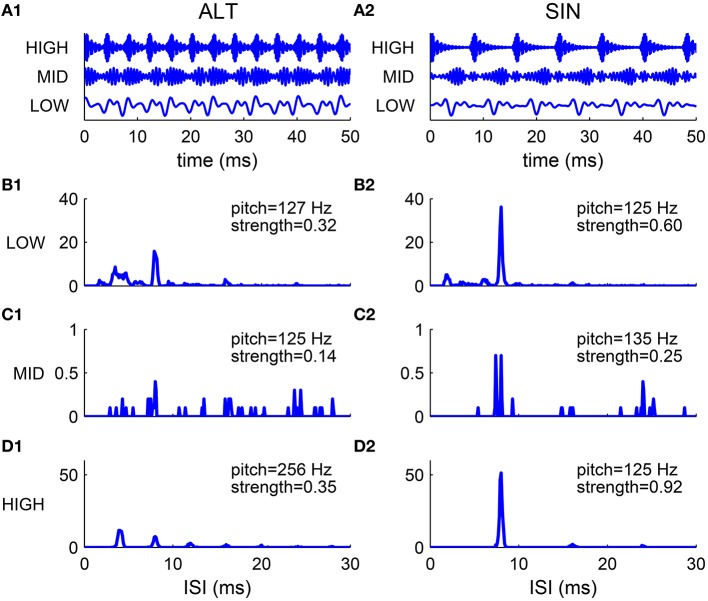
Figure 7.
Comparison of harmonic complexes with an alternating phase (ALT) (A1–D1) and those with a sine phase (SIN) (A2–D2) in different frequency regions. (A) Normalized stimulus waveforms of ALT (A1) and SIN (A2) complexes (F0 = 125 Hz) filtered in LOW (125–625 Hz), MID (1375–1875 Hz) and HIGH (3900–5400 Hz) frequency regions (extended frequency ranges for AN and SD units are used, for details see Methods). Envelope repetition rate of an ALT complex is one octave higher than its fundamental frequency, while envelope repetition rate of a SIN complex is the same as its F0. (B–D) Sums of ISI histograms of SDs over CF for complexes filtered in LOW (B1,B2), MID (C1,C2) and HIGH (D1,D2) frequency regions. Both ALT and SIN complexes have a pitch at F0 in the LOW frequency region, while the ALT complex has a pitch one octave higher than the SIN complex in the HIGH frequency region. Complexes in the MID frequency range have low pitch strength and low firing rates. Our modeling results are consistent with the psychophysical results in Shackleton and Carlyon (1994).