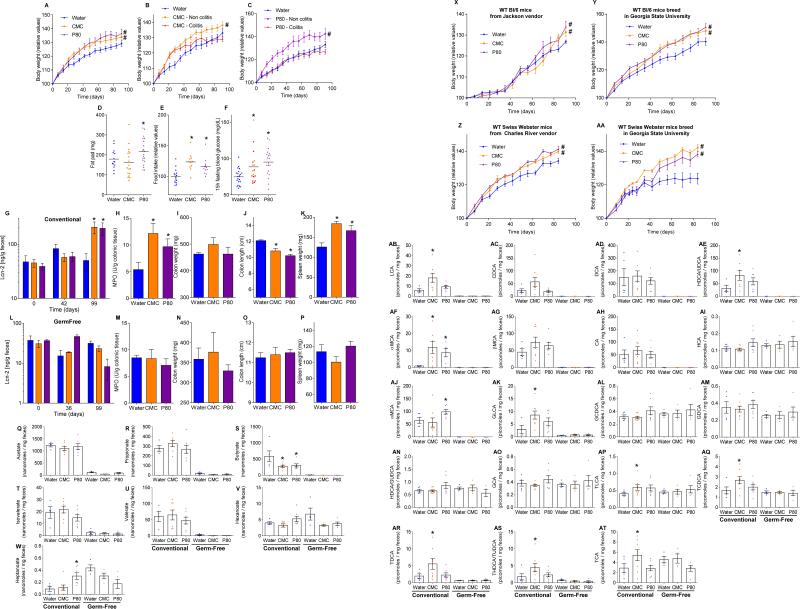
Extended data figure 9.
(A-F) Dietary emulsifiers promotes metabolic syndrome in IL10−/− mice. IL10−/− mice were exposed to drinking water containing CMC or P80 (1.0%) for 12 weeks. (A-C) Body weight over time, (D) fat-pad weight, (E) food intake measurement, and (F) 15-hours fasting blood glucose concentration. Data are the means +/- S.E.M. (for A, n=24, 18 and 21 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively; for B, n=14, 11 and 8 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively; for C, n=14, 9 and 9 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively; for D, n=14, 18 and 20 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively; for E, n=15, 11 and 12 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively; for F, n=21, 17 and 20 for water, CMC and P80-treated groups, respectively). Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with Sidak test (* indicates p<0.05 compared to water-treated group) or 2-way group ANOVA (# indicates p<0.05 compared to water-treated group). Points are from individual mice and red points in F represent mice with overt colitis. (G-P) Emulsifiers-induced low-grade intestinal inflammation was abolished under germ-free conditions. (G-K) Conventionally-housed and germ-free (L-P) Swiss-Webster mice were exposed to drinking water containing CMC or P80 (1.0%) for 12 weeks. (G, L) Fecal levels of the inflammatory marker Lcn2 over time, (H, M) MPO levels, (I, N) colon weights, (J, O) colon lengths and (K, P) spleen weights. Data are the means +/- S.E.M. (n=8 for conventionally-housed mice and n=4 for germ-free mice). Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with Sidak test or using two-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with Bonferroni test, * indicates p<0.05 compared to control group. (Q-W) Dietary emulsifiers induce perturbations in fecal short-chain fatty acid composition. Fecal short-chain fatty acids composition was analyzed at the Metabolomics Core of the University of Michigan. (Q) Acetate, (R) propionate, (S) butyrate, (T) isovalerate, (U) valerate (V) hexanoate and (W) heptanoate were analyzed. Data are the means +/- S.E.M. (n=5, 8 and 7 for water, CMC and P80 conventional mice-treated groups and n=4, 4 and 5 for water, CMC and P80 germfree mice-treated groups, respectively). Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with Sidak test, * indicates p<0.05 compared to water-treated group. (X-AA) Dietary emulsifiers promote metabolic syndrome in mice from different vendors. WT mice were exposed to drinking water containing CMC or P80 (1.0%) for 12 weeks. (X, Y) Body weight over time of Bl/6 mice used upon receipt from Jackson Laboratories (X) or bred at Georgia State University (Y). (Z, AA) Body weight over time of Swiss Webster mice used upon receipt from Charles River company (Z) or bred at Georgia State University (AA). Data in X are not used elsewhere in report, while data in Y, Z, and AA are from Figs 3A, extended data figure 8A-K, and 4A). Data are the means +/- S.E.M. (n=8 for Bl/6 mice used upon receipt from Jackson Laboratories, n=16 for Bl/6 mice bred at Georgia State University, n=10 for Swiss Webster mice used upon receipt from Charles River company, n=8 for Swiss Webster mice bred at Georgia State University). Significance was determined using 2-way group ANOVA (# indicates p<0.05 compared to water-treated group). (AB-AT) Dietary emulsifiers induce perturbations in fecal bile acids composition. Fecal bile acids composition was analyzed at the Metabolomics Core of the University of Michigan. (AB) Lithocholic acid (LCA), (AC) chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), (AD) deoxycholic acid (DCA), (AE) hyodeoxycholic acid / ursodeoxycholic acid (HDCA/UDCA), (AF) α-muricholic acid (α-MCA), (AG) β-muricholic acid (β -MCA), (AH) cholic acid (CA), (AI) hyocholic acid (HCA), (AJ) ω-muricholic acid (ω-MCA), (AK) glycolithocholic acid (GLCA), (AL) glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA), (AM) glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA), (AN) hyodeoxycholic acid / glycoursodeoxycholic acid (HDCA/GUDCA), (AO) glycocholic acid (GCA), (AP) taurolithocholic acid (TLCA), (AQ) taurine-conjugated chenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), (AR) taurodeoxycholic acid / Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TDCA/TUDCA), (AS) taurohyodeoxycholic acid, and (AT) taurocholic acid (TCA) were analyzed. Data are the means +/- S.E.M. (n=5, 8 and 7 for water, CMC and P80 conventional mice-treated groups and n=4, 4 and 5 for water, CMC and P80 germfree mice-treated groups, respectively). Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with Sidak test, * indicates p<0.05 compared to water-treated group.