Figure 6.
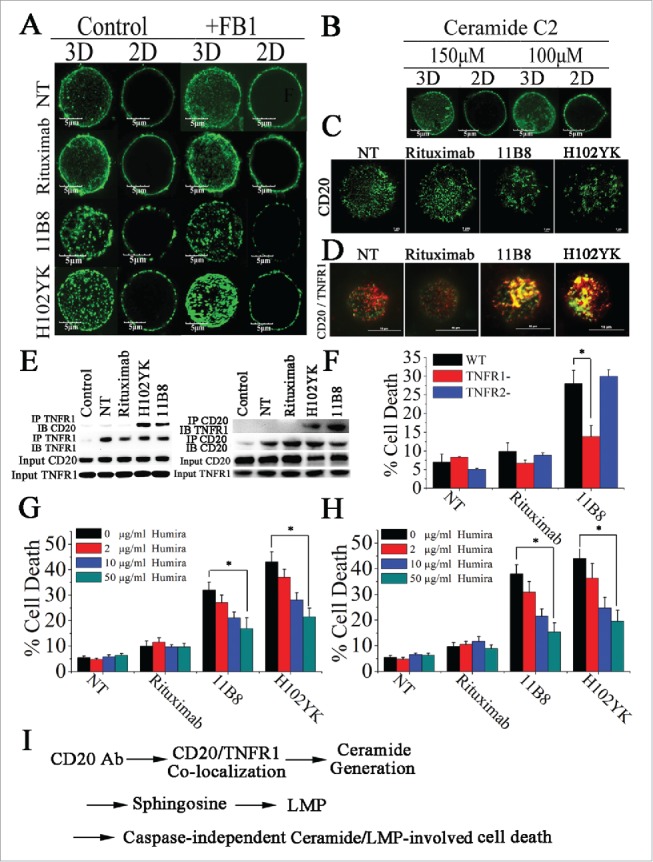
Colocalization of CD20 and TNFR1 initiated by CD20 mAbs is critical for initiation of lysosome-mediated cell death by CD20 mAbs. (A) Confocal images of the distribution of CD20 molecule after treatment with CD20 mAbs for 30 min. 3D reconstruction based on a confocal z-stack. (B) The impact of exogenous C2-ceramide on the spatial arrangement of CD20. Scale bars: 5 μm. (C) TIRF-SIM images of the distribution of CD20 in the bilayer before and after treatment with CD20 mAbs. Scale bars: 1 μm. (D) 3D-SIM images of the colocalization of CD20 (green fluorescence) and TNFR1 (red fluorescence) proteins before and after treatment with CD20 mAbs. The images were acquired by a structured illumination microscopy N-SIM (Nikon). Scale bars: 1 μm. (E) CD20 is recruited to the TNFR-1 signaling complex after treatment with type II CD20 mAbs and H102YK. The recruitment of CD20 protein was determined by western blot. Control: NT group used isotype antibody for IP, CD20 or TNFR1 antibody for IB. (F) The essential role of TNFR1 in induction of cell death triggered by type II CD20 mAbs. *p < 0.05. The inhibition of cell death by Humira after 48 h by Humira alone, 10 μg/mL rituximab, and rituximab variant in Raji (G) and Ramos (H) cells. Humira was added over a range of different concentrations for 2 h before the addition of mAbs. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05. (I) A proposed model role for initiation of lysosome-mediated cell death induced by CD20 antibodies.
