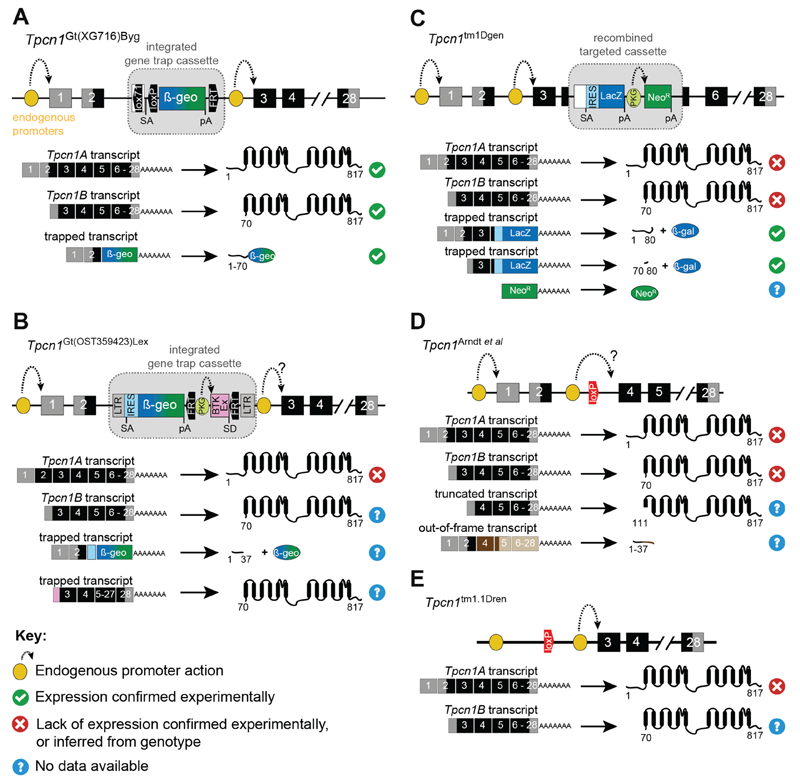
Figure 5.
Gene structure of Tpcn1 mutant mouse lines. The top section of each panel contains the gene structures of published Tpcn1 mutant mouse lines. Symbols for mutant alleles are based on MGI database nomenclature, except for Tpcn1Arndt et al. which is indicated by the publication reference where it was first described. (A) Gene trap line Tpcn1Gt(XG716)Byg (gene trap vector pGT1Lxf inserted in intron upstream from exon 3). (B) Gene trap line Tpcn1Gt(OST359423)Lex (gene trap vector VICTR 37, inserted in intron upstream from exon 3). (C) Targeted homologous recombination line Tpcn1tm1Dgen (targeted deletion of exons 4–5 with knock out cassette). (D) Cre loxP line Tpcn1Arndt et al. (Cre-mediated excision of floxed exon 3). (E) Tpcn1tm1.1Dren (Cre-mediated excision of floxed exon 2 containing the initiation codon for TPC1A). Predicted transcripts and proteins expressed from the mutant alleles are shown below the gene structures, on the right and left, respectively. Exons are represented by numbered boxes (grey – non-coding exons; black – coding exons; dark brown – coding exons for TPC-unrelated sequences; light brown – non-coding exons). Predicted proteins are depicted in: black (TPCs), brown (TPC unrelated), blue (β-gal), green (NeoR) or blue/green (β-geo); numbers represent first and last amino acid residues. BTK (cDNA for Bruton agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase), En2I (intron 1 of mouse En2 gene), FRT (flippase recognition target sequence), IRES (internal ribosomal entry site), LacZ (cDNA for β-galactosidase), LTR (long terminal repeats), loxP (loxP sequence), lox71 (mutant LoxP sequence), NeoR (cDNA for neomycin transferase), pA (poly-adenylation signal), PKGP (promoter of mouse Pkg gene), SA (splice acceptor), SD (splice donor).