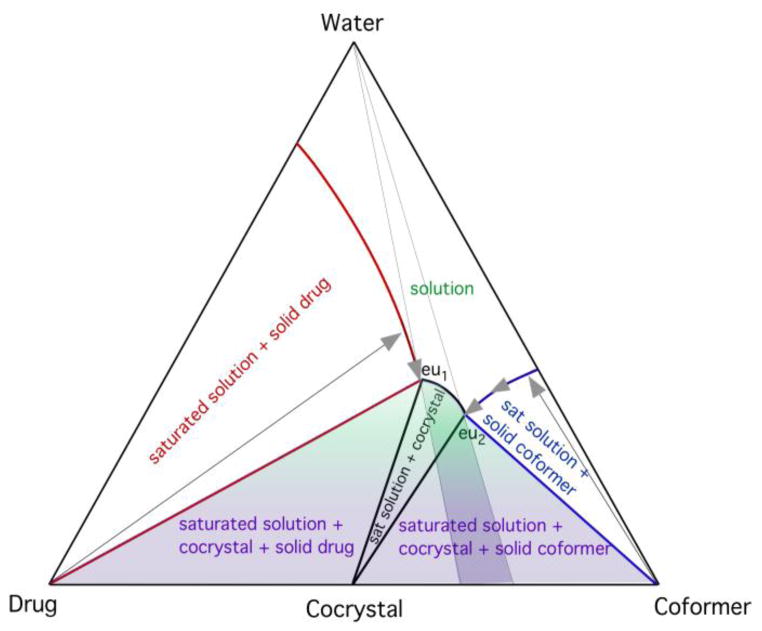
Fig. 10.
Triangular phase diagram illustrating the dissolution paths (arrows) that can lead to cocrystal stability regions (shaded areas). Solution compositions between the two eutectic points, eu1 and eu2, are favorable for cocrystal formation. Moisture content, drug, and coformer solubilities determine the dissolution path and supersaturation levels reached. The highest supersaturation for cocrystal is achieved by saturation with respect to both drug and coformer, conditions associated with water contents below the eutectic points. Reproduced from ref.[61] with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.