Figure 3.
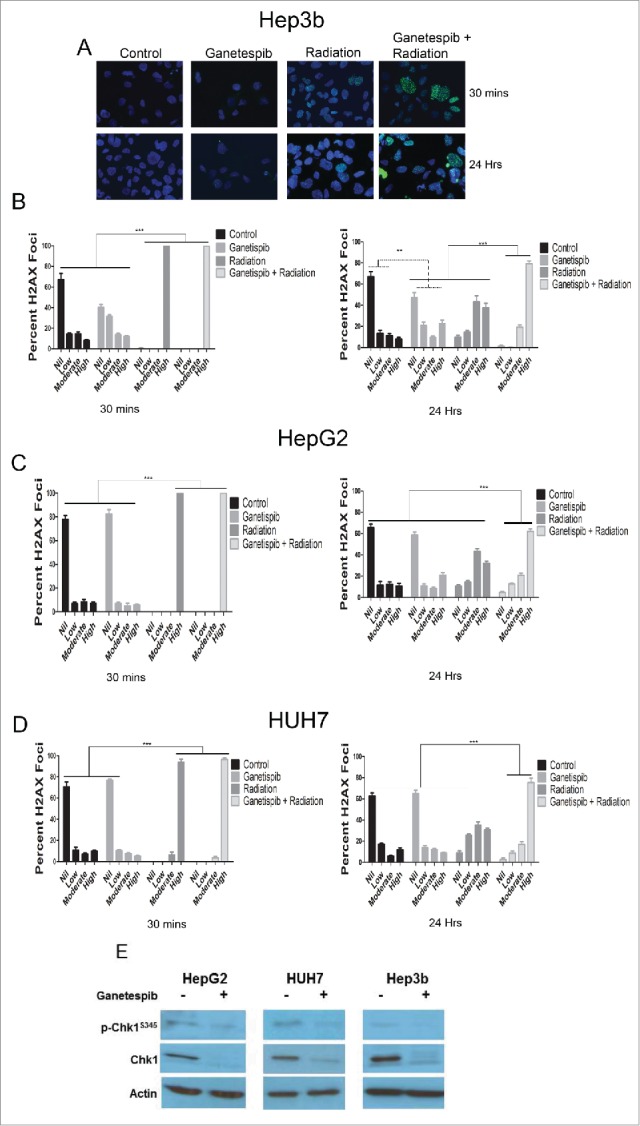
Ganetespib delays the repair of radiation-induced double strand breaks and downregulates the double strand break repair protein Chk1 in HCC cells. Immunofluorescence (IF) for γH2AX foci counterstained with DAPI and images captured using a fluorescent microscope. (A) Representative images are shown for Hep3B cell line at 30 minutes and 24 hours for each of the treatment arms; 20 nM ganetespib and/or 4 Gy of radiation when used. (B-D) Quantification of the percent of nuclei demonstrating no, low (<10 foci), moderate (10–25 foci) or high (>25) γ-H2AX foci per nuclei was quantified for all cell lines for each of the treatment arms and depicted graphically with standard error of the mean (SEM). For all cell lines, radiation alone and ganetespib-radiation resulted in a greater percentage of nuclei with a high number of γ-H2AX foci at 30 minutes when compared to any other treatment arm (p < 0.001, Fisher's exact test). At 24 hours, the ganetespib-radiation arm maintained a larger percentage of high γ-H2AX foci when compared to radiation alone (p < 0.001 for Hep3b and HUH7 and p = 0.0002 for HepG2, Fischer's exact test). (E) Cells were exposed to 24 hours of 50 nM ganetespib followed by an additional 24 hours prior to protein extraction and Western blotting for DNA damage response regulator p-Chk1-Ser345 and total Chk1 in all 3 HCC cell lines.
