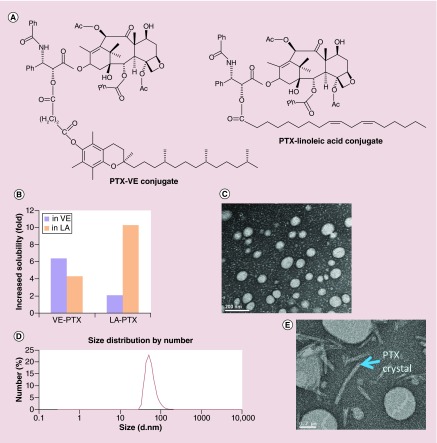
Figure 2. . The development of vitamin E-paclitaxel molecular-matched nanoemulsions.
(A) The molecular structure of VE-PTX and LA-PTX. (B) Increased folds of solubility of VE-PTX and LA-PTX compared with free PTX. (C) TEM images of VE-PTX NEs (VE-PTX/VE/TPGS = 160/900/360, w/w). (D) The average particle size and size distribution of VE-PTX NEs (pH 7.4 PBS as solvent, 1.6 mg/ml VE-PTX NEs were diluted about 50-fold) were determined by quasielastic laser light scattering with a Malvern Zetasizer at 25°C (n = 3). (E) TEM images of PTX NEs (PTX/VE/TPGS = 10/900/360, w/w).
LA-PTX: Linoleic acid-paclitaxel; NE: Nanoemulsion; TEM: Transmission electron microscopy; TPGS: D-α tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate; VE-PTX: Vitamin E-paclitaxel.