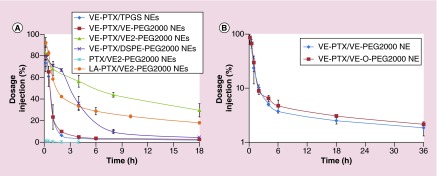
Figure 4. . Pharmacokinetic studies of molecular-matched and molecular-mismatched emulsions.
(A) The PK profiles of PTX emulsion and VE-PTX PEGylated NEs (n = 3). The mice were injected intravenously with different formulations (equal dose of 10 mg PTX/kg) containing 2 µCi 3H labeled PTX (or 3H labeled PTX-VE). PTX emulsions (PTX/VE/TPGS/VE2-PEG2000 = 5/900/288/110, w/w); VE-PTX/TPGS NEs (VE-PTX/VE/TPGS = 100/900/340, w/w). All other VE-PTX PEGylated NEs contained the same molar ratio with VE-PTX/TPGS NEs, except that 20% mol TPGS was replaced with VE-PEG2000, DSPE-PEG2000 and VE2-PEG2000. (B) PK comparison between VE-PTX NEs PEGylated with VE-O-PEG2000 and VE-PEG2000 (n = 3). The mice were injected intravenously with the dose of 16 mg VE-PTX/kg containing 2 µCi 3H labeled PTX-VE. VE-PTX NEs (VE-PTX/VE/TPGS/VE2-(O)-PEG2000 = 100/900/288/90, w/w).
DSPE-PEG2000: 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[amino(polyethylene glycol)-2000]; NE: Nanoemulsion; PK: Pharmacokinetic; PTX: Paclitaxel; TPGS: D-α tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate; VE: Vitamin E; VE-PTX: Vitamin E-paclitaxel.