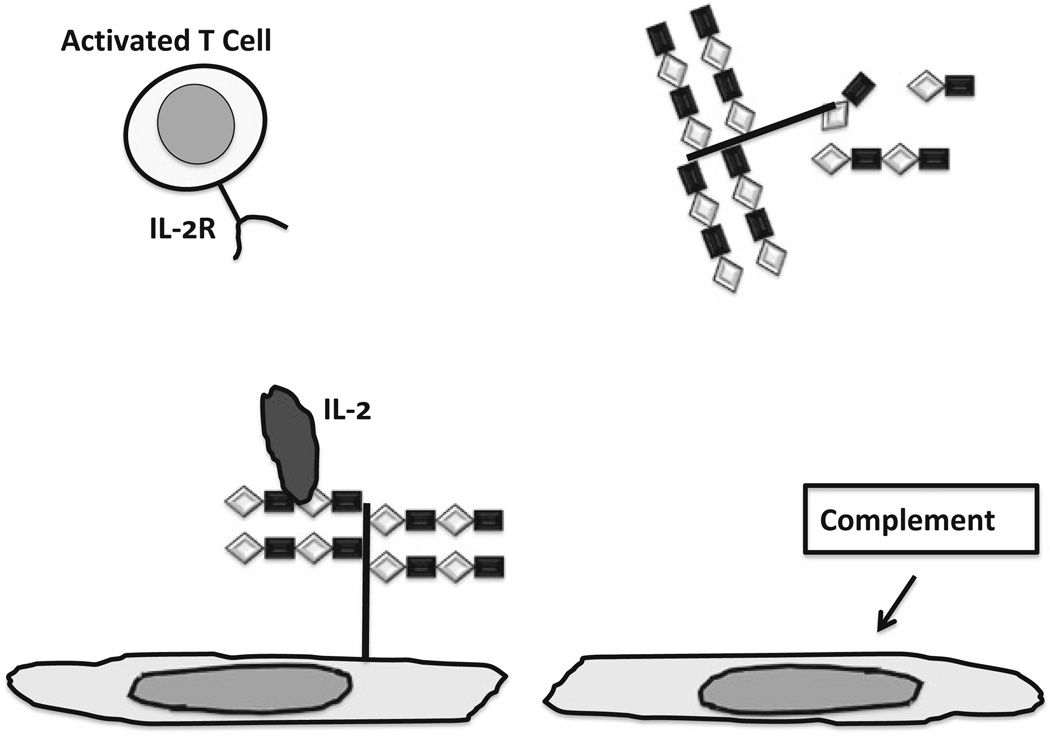
Fig. 8.3.
Impact of heparan sulfate proteoglycan and shedding of heparan sulfate proteoglycan and glycosaminoglycan on control of cellular immunity. Left : Intact heparan sulfate chains bind IL-2, which can cause activated T cells to undergo apoptosis, contributing to immunological tolerance. Right : Loss of heparan sulfate caused by activation of complement deprives endothelium of IL-2, allowing activated to cells to attach, transmigrate and exert effector functions