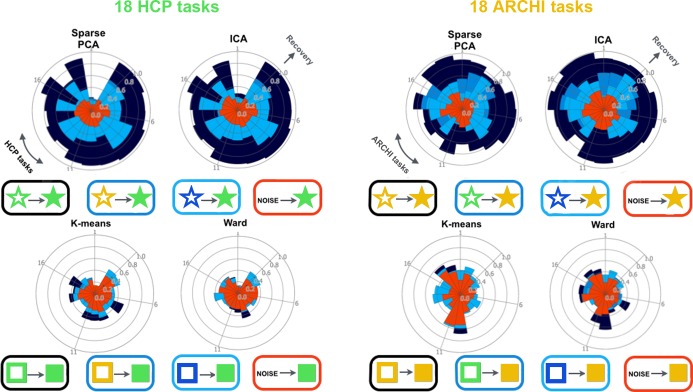
Fig 8. Task-rest correspondence: Recovery performance across network and region atlases.
40 networks (upper row) were discovered in independent component analysis (ICA) and sparse principal component analysis (sparse PCA). 40 regions (lower row) were derived from k-means and ward clustering based on four diverging types of neural activity data. Network and region atlases were derived from i) identical task-data as positive test (dark blue), ii) non-identical task-data (medium blue), iii) resting-state data (light blue), and iv) Gaussian noise as negative test (red). The ensuing networks and regions were then used to create a feature space of neural activity patterns for 18-task classification (l1-penalized support vector machines, multi-class, one-versus-rest) and subsequently measure the per-task recovery performance. The recovery performance of all 18 tasks (radial columns) is measured by the Pearson correlation between the model-derived task activity maps and the average first-level task map. As an important observation, network dictionaries derived from different tasks and from rest data were similarly successful in recovering whole-brain activity during diverging experimental tasks, while specialized regions achieved much worse recovery performances in both datasets. See S11 and S12 Figs for additional analyses.