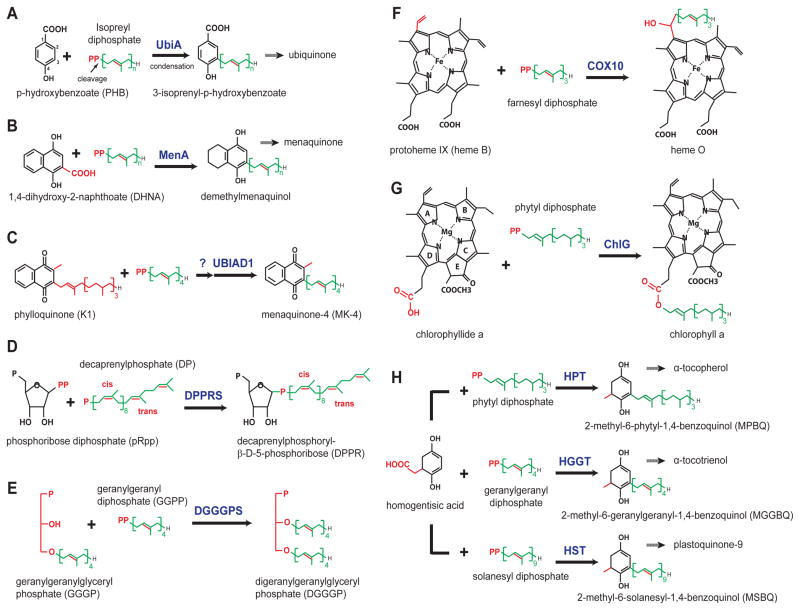
Figure 2. Reactions catalyzed by the UbiA superfamily enzymes.
Key features in different chemical structures are shown in red, and the prenyl or phytyl chains in green. (A) UbiA cleaves the diphosphate group from XPP and fuses it to the meta-position of PHB [4,23]. (B) MenA catalysis involves a decarboxylation step [24]. (C) UBIAD1 catalysis may involve side-chain exchange [7]. (D) DPPR synthase fuses a ribose to a unique prenyl substrate with several cis-bonds [20]. (E) DGGGP synthase fuses two linear substrates [25]. (F–G) COX10 and ChlG prenylate heme and chlorophyl acceptors, respectively, both of which have large porphyrin rings [22,27]. (H) Homogenisate transferases, HPT, HGGT, and HST, use different prenyl or phytyl diphosphates as donor substrates [28].