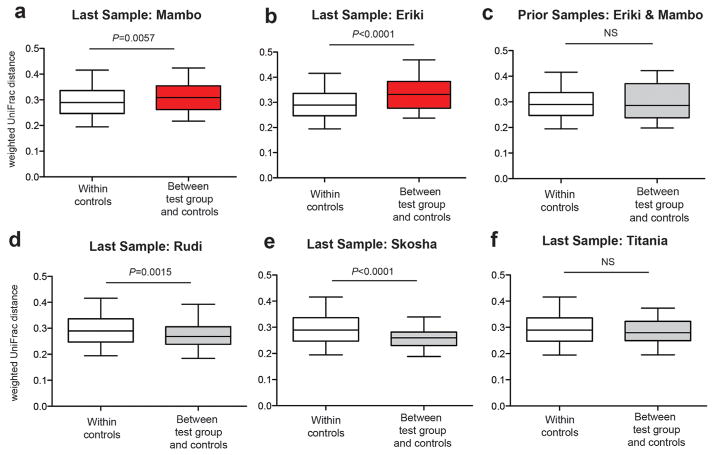
Fig. 5.
Pronounced compositional shifts in the gut bacterial communities of two SIVcpz-infected chimpanzees shortly before their disappearance. (a) Pairwise weighted UniFrac distances from the last fecal sample of Mambo (test group), an SIVcpz-infected chimpanzee who disappeared two months after sample collection, were compared to pairwise weighted UniFrac distances of fecal samples (N = 98) from all chimpanzees who were sampled more than 8 months before their death (control group). Box plots show the median, upper, and lower quartile ranges with whiskers indicating 95% confidence intervals (CI). Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann–Whitney U-test. Red indicates significantly increased beta diversity. (b) Analysis as in (a), but comparing pairwise weighted UniFrac distances from the last fecal sample of Eriki (test group), an SIVcpz-infected chimpanzee who also disappeared 2 months after sample collection, to the same controls. (c) Analysis as in (a), but comparing weighted UniFrac distances from earlier fecal samples (collected more than 8 months before death) from Mambo and Eriki (test group) to the same controls. (d, e, and f) Analysis as in (a), but comparing pairwise weighted UniFrac distances from the last fecal sample of Rudi, Skosha, and Titania (test groups), SIVcpz-infected chimpanzees who disappeared 5, 4, and 7 months after sample collection, respectively, to the same controls.