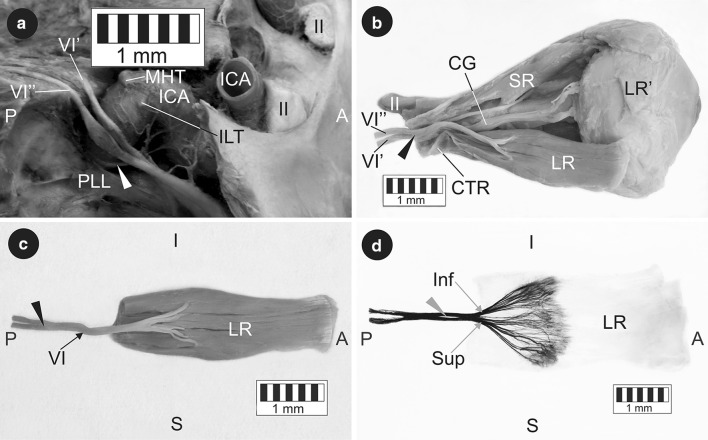
Fig. 1.
The course and innervation pattern of the duplicated abducens nerve. a Intracranial segments. The clival dura mater and the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus were removed. The main branches of the cavernous segment of the internal carotid artery were carefully removed during the dissection in order to better visualise the course of the abducens nerve. White arrowhead internal carotid plexus. b Intraorbital segments. A lateral incision of the common tendinous ring exposed the point where both trunks of the duplicated abducens nerve merged. Black arrowhead the site of fusion of both trunks of the duplicated abducens nerve. c Isolated lateral rectus muscle specimen. The inner surface of the muscle was visualised along with the abducens nerve sub-branches reaching it. Black arrowhead the site of fusion of both trunks of the duplicated abducens nerve. d Intramuscular innervation pattern of the lateral rectus muscle. Sihler’s staining. View of the internal muscle surface. A slight deformation of the muscle results from the technological process of staining. Grey arrowhead short ‘split’ within intraconal segment of the abducens nerve. A anterior, P posterior, I inferior, S superior, II optic nerve, VI single trunk (intraconal segment) of the abducens nerve, VI’ medial trunk of the duplicated abducens nerve, VI” lateral trunk of the duplicated abducens nerve, CG ciliary ganglion, CTR common tendinous ring, ICA internal carotid artery, ILT origin of the inferolateral trunk, LR lateral rectus muscle, LR’ insertion of the lateral rectus, MHT origin of the meningohypophyseal trunk, PLL petrolingual ligament, SR superior rectus muscle, Inf sub-branches to the inferior compartment of the lateral rectus, Sup sub-branches to the superior compartment of the lateral rectus