Fig. 6.
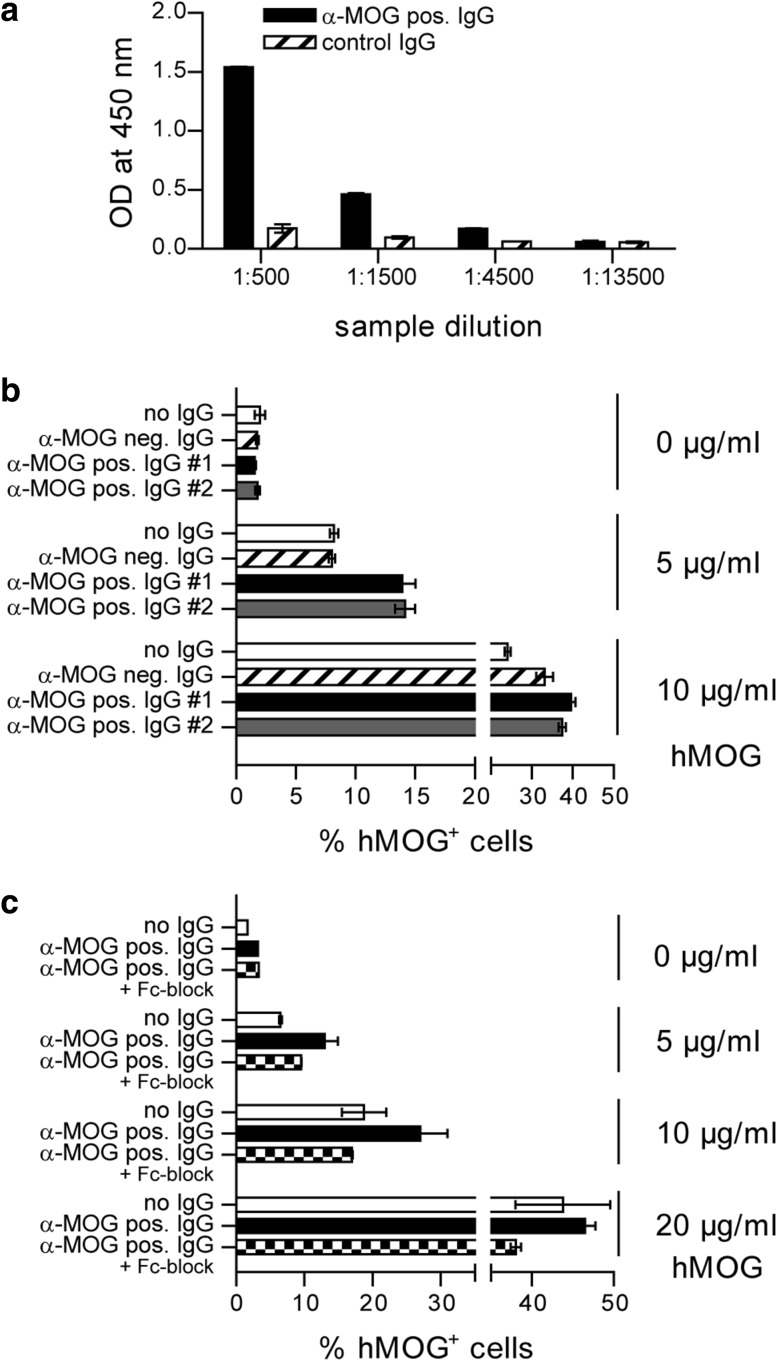
IgG isolated from patients with NMOSD facilitate recognition of hMOG protein. a Detection of Ab against hMOG in a purified IgG fraction of a patient with NMOSD (α-MOG pos. IgG) by ELISA. Plate-bound Ab were detected with anti-human IgG Ab directed against the Fc part. For ELISA, intravenous IgG (control IgG) served as negative control. b Phagocytosis of hMOG-DyLight-405 by WT BMDM. Cells were incubated with hMOG-DyLight-405 in the presence of IgG samples from NMOSD patients containing anti-MOG Ab (α-MOG pos. IgG #1 and #2) or an anti (α)-MOG Ab negative (neg.) IgG preparation from a healthy individual (mean % of hMOG-DyLight-405 positive (hMOG+) APC, gated on intact CD11b+/CD11c+ cells). Representative data set shown; p < 0.05 for α-MOG pos. IgG #1 vs. α-MOG neg. IgG and α-MOG pos. IgG #2 vs. α-MOG neg. IgG at 5 µg/ml hMOG (t test). c Phagocytosis of hMOG-DyLight-405 by WT BMDM. Cells were incubated with hMOG-DyLight-405 in the presence of anti-MOG positive IgG #2 or a combination of anti-MOG positive IgG #2 and Fcγ receptor blocking anti-CD16/CD32 Ab (8.18C5 + Fc-block; mean % of hMOG+ APC, gated on intact CD11b+/CD11c+ cells)