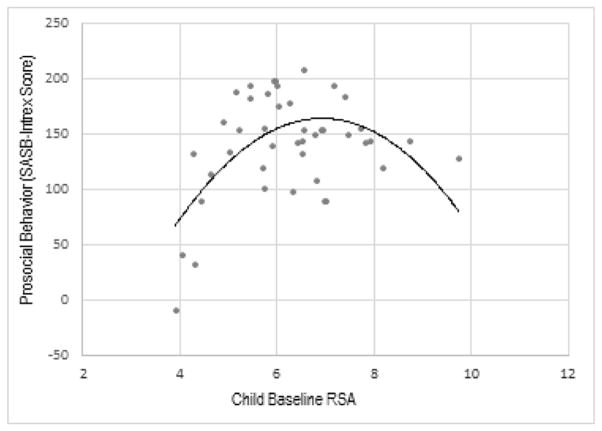
Figure 4.
Changes in RSA from baseline to interaction with a) mother and b) with a research assistant (RA) in children with low and high cumulative risk scores.
For illustrative purposes, children are grouped by high (> 3 risk factors) and low (3 or fewer risk factors) cumulative risk scores. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. While cumulative risk was not associated with baseline RSA, children with higher levels of cumulative risk showed a greater drop in RSA during the social interaction episodes.