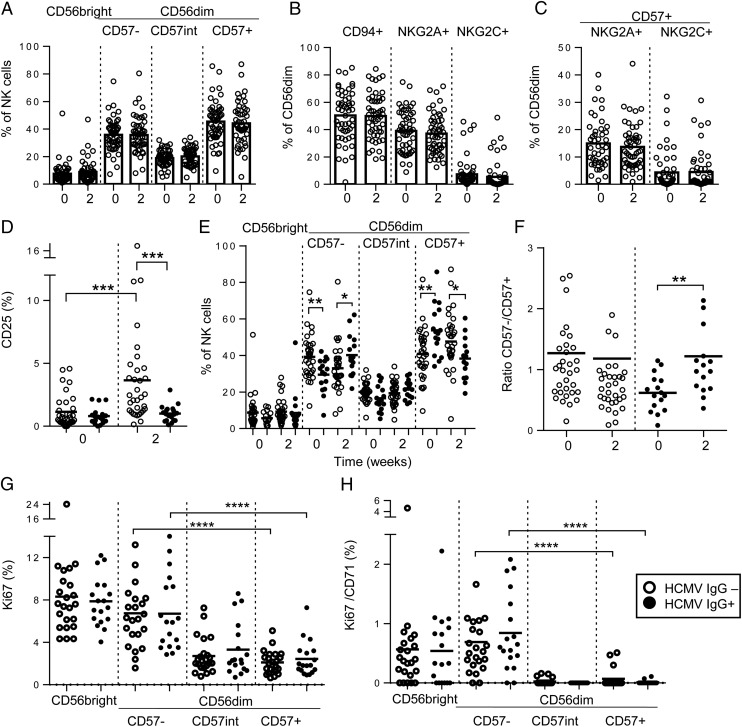
FIGURE 9.
Impact of influenza vaccination and HCMV infection status on ex vivo NK cell-surface phenotype. Frequencies of CD56bright and CD56dimCD57-defined subsets (A), CD94-, NKG2A-, and NKG2C-expressing NK cells (B), and NKG2A+CD57+ or NKG2C+CD57+ NK cells (C) were measured directly ex vivo before (0) or 2 wk after vaccination for all 52 study subjects. NK cells from HCMV− (open circles; n = 33) and HCMV+ (closed circles; n = 19) subjects were compared for ex vivo frequencies of CD25+ cells (D), proportions of cells in each subset (E), and the ratio of CD56dimCD57− to CD56dimCD57+ cells before (0) or 2 wk after vaccination (F) and for frequencies of NK cells in each subset expressing Ki67 (G) or Ki67 in combination with CD71 (H) 2 wk after vaccination. Bars represent mean values. Mann–Whitney U test was used for intergroup comparisons, and trend analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with correction for repeated measures. ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.