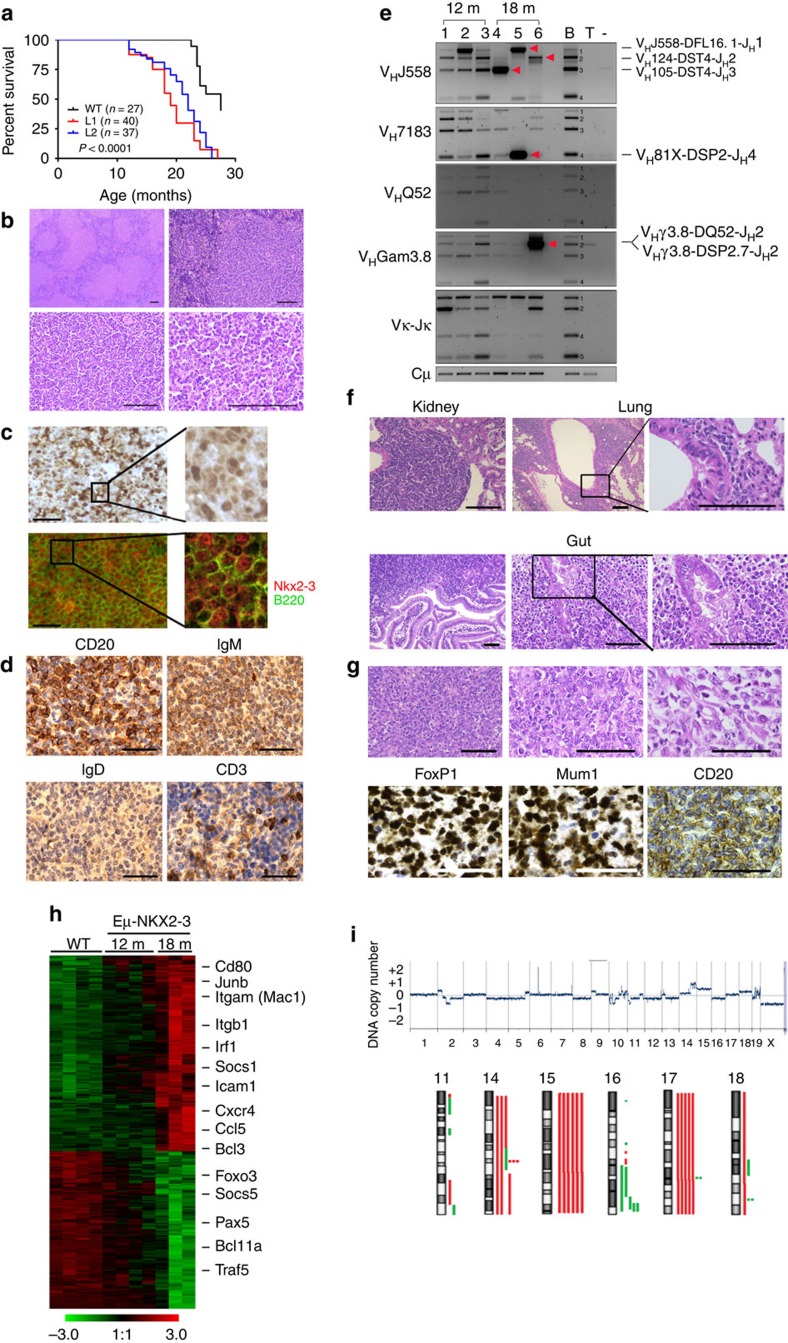
Figure 3. Eμ-NKX2-3 mice develop human-like marginal-zone lymphomas.
(a) Kaplan–Meier overall survival curves for the two Eμ-NKX2-3 transgenic lines and WT mice. (b) Haematoxilin-eosin (H&E) staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded spleen tissues of Eμ-NKX2-3 transgenic mice. Scale represents 100 μm in all cases. (c) Immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) studies of transgenic spleens using NKX2-3 and B220 antibodies. (d) IHC studies of transgenic spleen biopsies using CD20, IgD, IgM and CD3 antibodies. (e) Detection of Ig gene rearrangements by PCR on genomic DNA from CD19+ cells isolated from transgenic spleens in 12- and 18-month-old mice. VDJH clonal rearrangements were identified by direct sequencing (marked with red arrowheads). Approximate sizes for WT B-cell V(D)J rearrangement bands (labelled 1 to 4) are Jh1: 1800, bp, Jh2: 1200, bp, Jh3: 800 bp and Jh4: 300 bp. B and T, healthy murine B (CD19+) and T (CD3+) lymphocytes, respectively. (f) H&E staining of extranodal lymphomas developed in the kidney, the lung and the gut, showing lymphoepithelial lesions. (g) H&E staining of spleen tissue biopsies showing transformation areas resembling DLBCL. IHC showed positive staining for using CD20, FoxP1 and Mum1 (Irf4), whereas Gcet1, Bcl10 and Bcl6 expression was not observed. (h) Heat-map image of gene expression profiling data showing the 12- and 18-month-old transcriptional signatures in comparison to WT splenic B lymphocytes. (i) Whole-genome array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) analysis of isolated CD19+ cells from nine clonal splenic lymphomas developed in 18-month-old transgenic mice. Chromosomal losses and gains are shown in green and red colours, respectively (bottom). A representative example is shown (top). m, month.