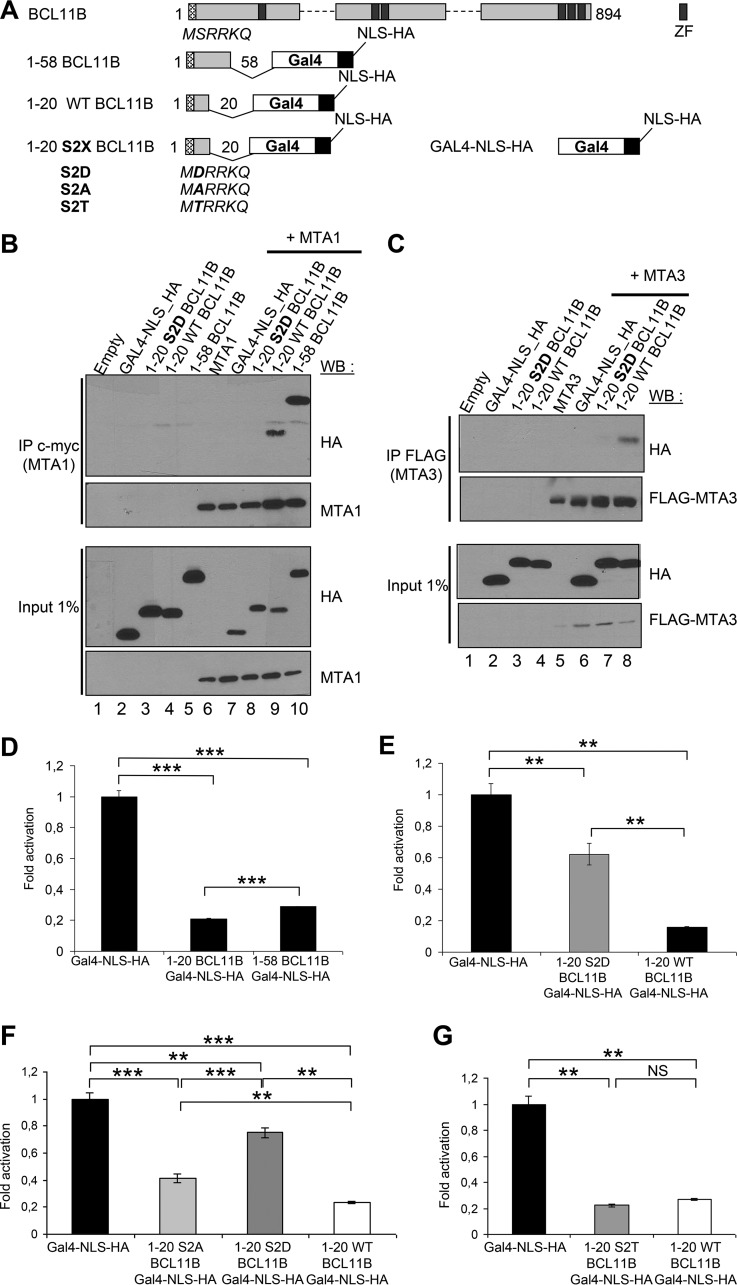
FIG 2.
Ser2 in the conserved N-terminal motif of BCL11B is essential for its interaction with MTA1 and MTA3 and for its transcriptional repression activity. (A) Schematic drawing of the BCL11B-Gal4 (DNA-binding domain)-NLS (nuclear localization signal)-HA fusion proteins. ZF, zinc finger. (B) A phosphomimetic point mutation S2D in the BCL11B N-terminal domain inhibits its interaction with MTA1. After transfection with the indicated expression vectors, HEK293T cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-myc antibodies (IP c-myc). Immunoprecipitated samples and 1% of whole-cell extracts (Input) were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) The BCL11B-MTA3 interaction is also negatively regulated by the S2D mutation. A similar experiment was performed in HEK293T cells with a FLAG-MTA3 plasmid and the BCL11B-Gal4 chimeras. (D) The conserved BCL11B N-terminal domain represses transcription. The transcriptional activity of BCL11B-Gal4 constructs was tested by transient luciferase reporter assays in HEK293T cells. The results represent the mean values from three independent transfections in triplicate. (E) The S2D phosphomimetic mutation in the BCL11B N-terminal domain partially inhibits its transcriptional repression potential. A similar luciferase reporter assay was conducted in HEK293T cells with the wild-type (WT) 1-20 BCL11B and the S2D point mutant. (F and G) Repression potential of the various S2X point mutants BCL11B N-terminal domain. Luciferase reporter assays were conducted with the S2A, S2D, S2T, and WT BCL11B-Gal4 constructs as described above. Values that are statistically significantly different are indicated by bars and asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Values that are not statistically significantly different (NS) are also indicated.