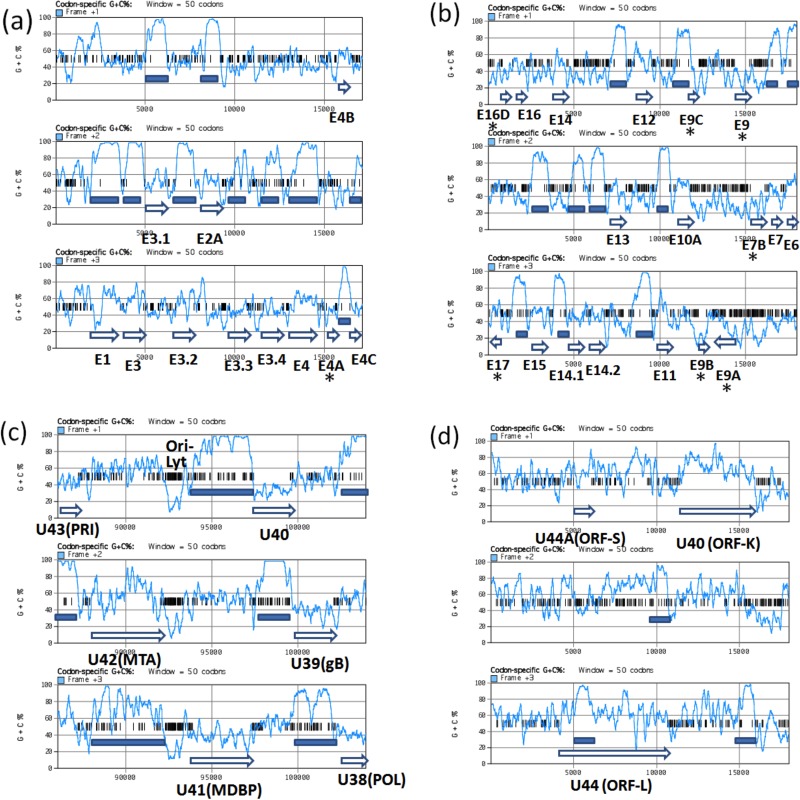
FIG 4 .
Codon-specific scanning GC content panels showing the wobble codon GC bias effect across selected representative segments of the EEHV4(Baylor) genome. Diagrams showing the percent G-plus-C content of each of the three potential translated codon frames across four selected 18-kb segments of the EEHV4B(Baylor) genomic DNA sequence as implemented under the codon-specific G-plus-C percent toolbox item in MacVector 12. Short vertical bars indicate forward direction terminators. Annotated ORF positions and sizes are denoted by open arrows. Highly GC-biased wobble position blocks with average values between 80 and 100% are marked with solid bars. For a hypothetical ORF with an initiator codon beginning in frame 1 at position x in the diagram, the wobble position codons are represented by the succeeding frame 3 line (or frame 1 for a frame 2 initiator and frame 2 for a frame 3 initiator). (a) Forward-directed strand across coordinates 1 to 18000 at the extreme left side encompassing 10 out of 11 rightward-oriented genes from E1 to E4C, including E4 (vGCNT1) with high wobble position GC bias. (b) Inverted segment of the complementary strand across coordinates 37000 to 19000 encompassing predominantly leftward-oriented genes (16 between E6 and E16D) and two rightward-oriented genes (E9A and E17), including 11 genes displaying uniformly high wobble codon GC bias plus seven genes in two blocks, E7B-E9 (vOGT)-E9A-E9B-E9C and E16D (vECTL)-E17-E17A, that do not display wobble GC bias (all of the latter are labeled with asterisks). (c) Forward strand across coordinates 86000 to 104000 encompassing six rightward-oriented core region genes, U43 (PRI) to U38 (POL), with high wobble position GC bias on either side of the predicted novel Ori-Lyt domain. (d) Inverted segment of the complementary strand from the extreme right side across coordinates 187867 to 205894 encompassing U44A (ORF-S), U44 (ORF-L), and U40 (ORF-K). The only three high-GC-bias wobble codon blocks found within this region occur in ORF-S and in the conserved C-terminal domains of ORF-L and ORF-K (marked with solid bars).