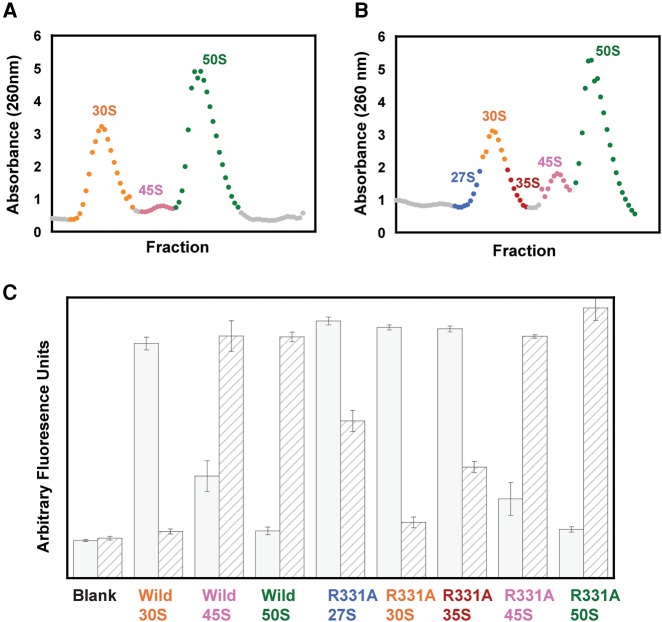
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of ribosomal RNA in E. coli cells overexpressing wild-type or R331A DbpA. (A) Ribosome profile of the cells overexpressing wild-type DbpA. (B) Ribosome profile of the cells overexpressing R331A DbpA. The ribosome profiles of the cells overexpressing wild-type or R331A DbpA contained only 1 mM MgCl2, which resulted in the ribosomes dissociating into separate subunits. (C) Fluorescent assay with binary deoxyribozyme (biDz) sensors. The fluorescence signals for biDz-16S and biDz-23S are shown as solid gray bars and striped bars, respectively. The amount of RNA used for each particle was normalized to match the fluorescent output of the dominant RNA species (16S rRNA in 27S, 30S, and 35S peak fractions, and 23S rRNA in 45S and 50S fractions) in the particle. Thus, the ratio of 23S:16S rRNA for each particle, which will not change with concentration, should be used to compare the particles. These data show that 23S RNA is present both in the right and the left shoulders of the 30S peaks on the cells overexpressing R331A DbpA; no 23S RNA was observed migrating with the middle fractions from 30S peak of the cells overexpressing R331A DbpA or the whole 30S peak from the cells overexpressing wild-type DbpA.