Figure 6.
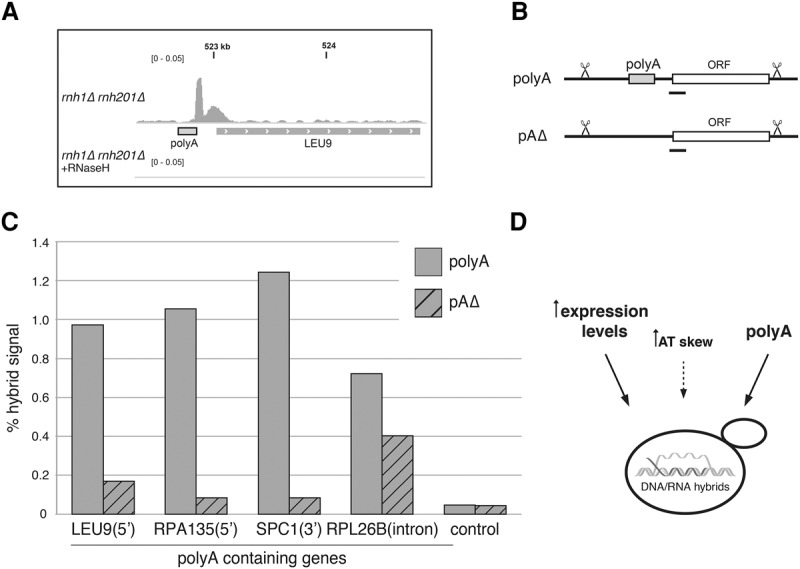
PolyA tracts directly affect hybrid formation. (A) PolyA-associated hybrid region. Snapshot of a representative polyA-associated hybrid 5′ of LEU9 showing the hybrid signal from rnh1Δ rnh201Δ (top) and rnh1Δrnh201Δ treated with RNase H in vitro (bottom). (B) Schematic of a locus containing a polyA tract (polyA) and a locus with a polyA tract seamlessly deleted (pAΔ). The locations of DRIP-qPCR amplicons are indicated with black bars. (C) Hybrid signal measured by DRIP-qPCR at polyA-containing genes. Hybrid signal was determined in rnh1Δrnh201Δ strains containing polyA tracts (solid bars) and deleted for the polyA (hatched bars) at the indicated genes. (D) Model of hybrid-promoting sequence features in yeast.
