Figure 2. Predicted probability of opioid misuse (with 95% confidence interval) by lower- and high-volume opioid prescribers.
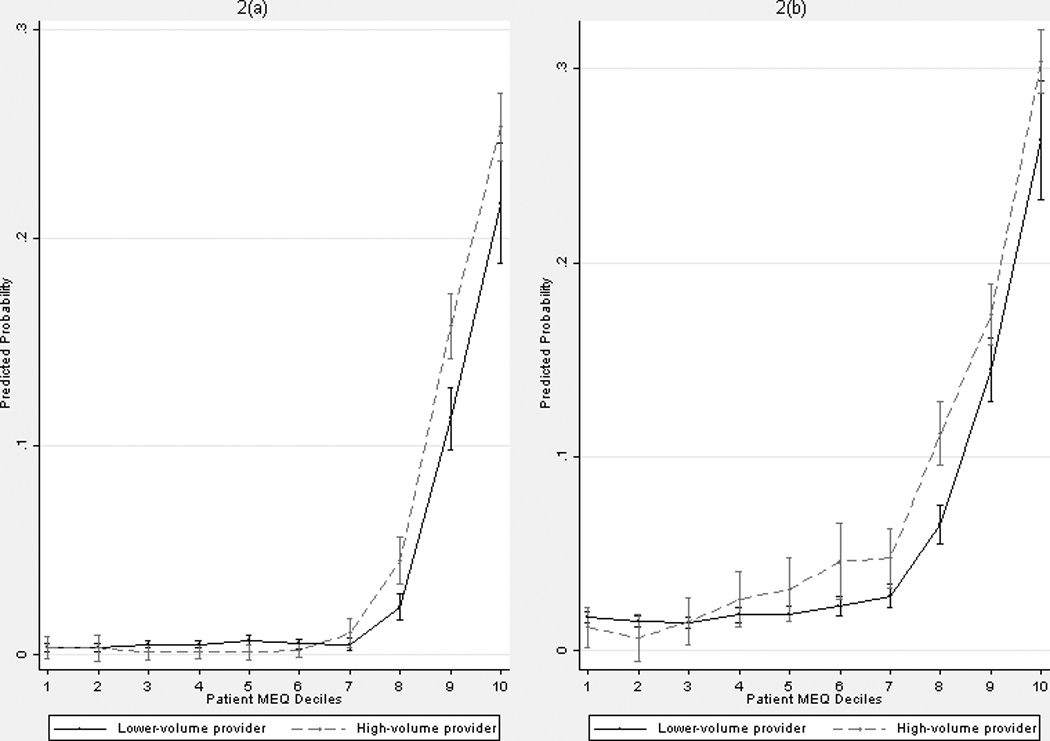
(a) Opioid prescription overlap
(b) Opioid/benzodiazepine overlap
a High-volume providers are the ones in the top MEQ decile with 68,383mg or higher MEQ.
b Each equation was estimated using an ordinary least squares regression, with standard errors clustered on provider. Each outcome variable was then predicted and then how the predicted outcome varies across patient MEQ decile and lower-volume/high-volume provider was presented.
