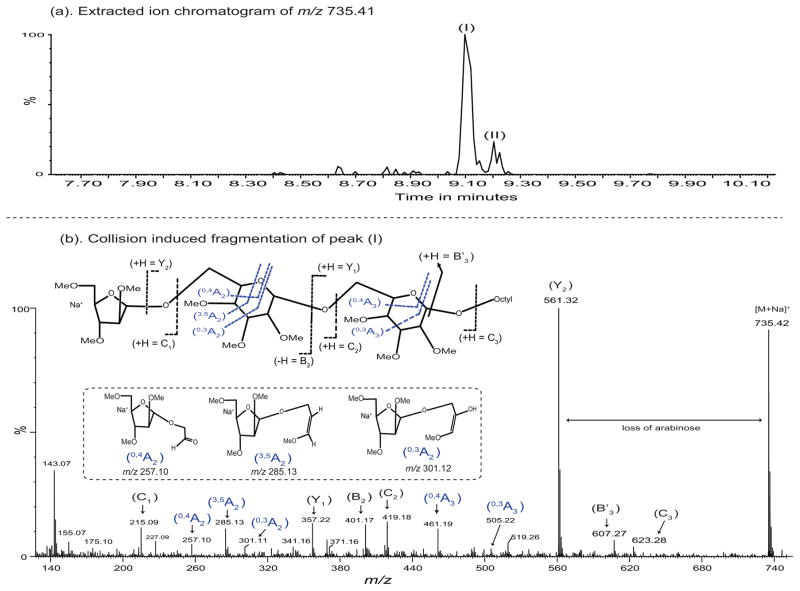
Figure 4. MS/MS analysis of the arabinosylated acceptor (1).
The [M+Na]+ion of the major arabinosylated product at m/z 735.42 (a) was subjected to collision-induced fragmentation resulting in the spectrum shown in (b). All ions are present in the sodiated form of otherwise neutral fragments (except possibly m/z 143 which might be the terminal arabinosyl C-1 cation minus methanol). The formation and structure of the fragments of the product where the arabinosyl residue is attached at O-6 of what was the terminal mannosyl residue is shown in (b). As discussed in the text, the MS/MS spectrum strongly suggests that the structure shown in (b) is correct and is supported by the GC/MS data shown in Supplementary Figure 1. The MS/MS spectrum fragment ions obtained by glycosidic and cross-ring fragmentation were identified according to Domon and Costello nomenclature26. The formation of B′3 ion at m/z 607.23 was identified as previously described27.