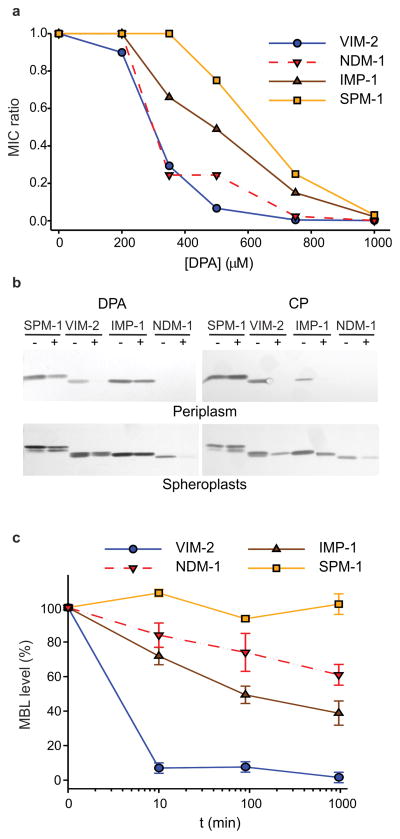
Figure 1. Zn(II) deprivation reduces bacterial antibiotic resistance and causes degradation of MBLs in the Escherichia coli periplasm.
(a) Relative MIC values of cefotaxime for E. coli cells expressing VIM-2, NDM-1, IMP-1 or SPM-1 in growth medium supplemented with different concentrations of the metal chelator DPA. MIC ratio values were calculated as described in the Methods section. Data correspond to three independent experiments, with standard errors ≤16% of each data point. (b) Western blot analysis of MBL levels in cells grown under conditions equivalent to those used for MIC assays, with (+) and without (–) addition of 350 μM DPA or 250 μg/mL CP to the growth medium. Original Western Blots are displayed in Supplementary Figure 11 (c) Relative MBL levels in the bacterial periplasm as a function of time after addition of 1000 μM DPA. Protein levels were quantified from Western blots (Supplementary Fig. 1b), normalized to control samples not treated with DPA, and plotted as the % of initial protein content remaining after treatment with DPA. Data correspond to three independent experiments and are shown as mean ± s.e.m.