Figure 6.
Induction of CD56 Expression, Colony-Forming Efficiency and Myogenic Differentiation of FACS Sorted Muscle-Derived “MSCs,” and In Vivo Localization of ALP, CD146, and PAX 7
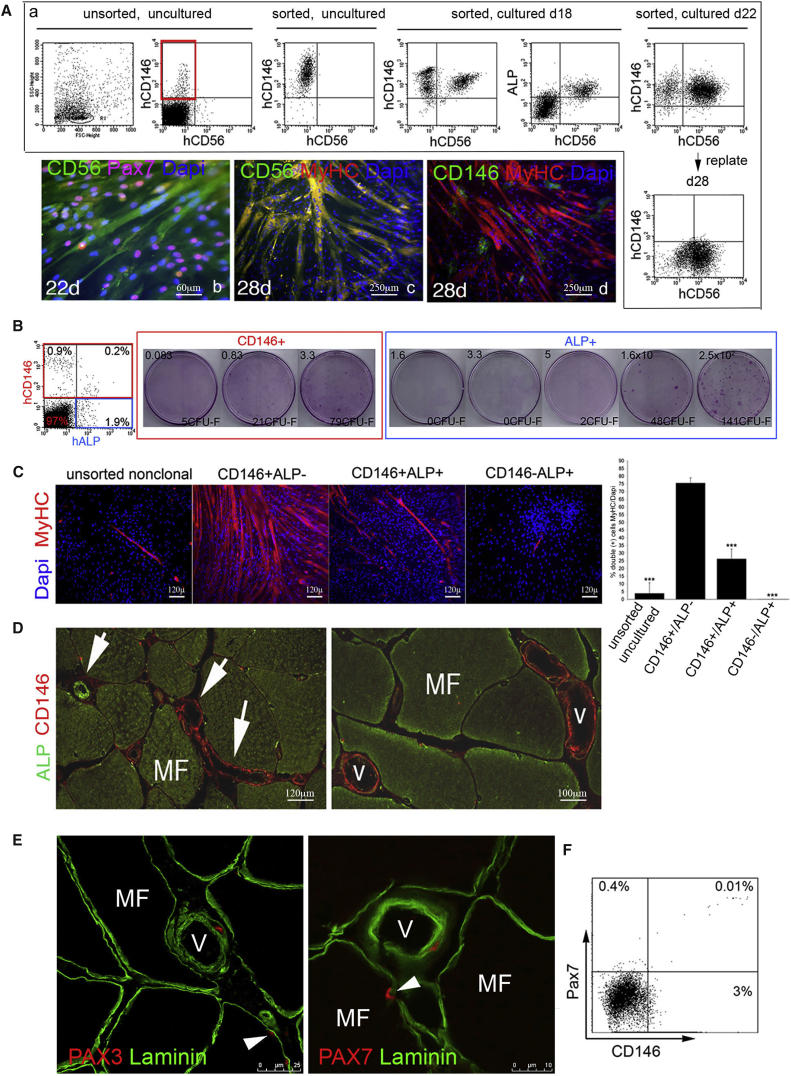
(A) Induction of the satellite cell marker, CD56, in cultures of CD34−/CD56−/CD146+ cells by FACS and fluorescent immunocytochemistry. Red box indicates the population of CD146+/CD56− cells used to establish the cultures. By FACS, co-expression of CD56 in a subset of CD146- and ALP-expressing cells is detectable after 18 days in culture, and the percentage of CD146+/CD56+ cells increases over time. Upon replating cultured CD146+/CD56+ cells at high density with 20% FBS, CD146 expression is turned off, whereas CD56+ expressing cells remain detectable. By fluorescent immunocytochemistry, subconfluent cultures express CD56 (green) and PAX7 (purple when colocalized with the blue nuclear stain, DAPI) (22 days in culture), and when replated at high density with 20% FBS, myotubes with numerous nuclei (DAPI staining) express myosin heavy chain (MyHC, red), co-localizing with CD56 (green) resulting in yellow. At a terminal stage of differentiation (26–28 days in culture), CD146 expression is barely detectable. Scale bars represent 60 μm or 250 μm as indicated.
(B) FACS of collagenase-released cell suspensions of muscle. Co-expression of CD146 and ALP, in human MU cell suspensions before culture. CFE assay of FACS-sorted CD146−/ALP+ cells and CD146+/ALP+ cell subsets. CD146+/ALP+ and CD146−/ALP+ cells were plated at different cell densities. Numbers (upper left of each panel) indicate the number of cells plated/cm2.
(C) When unsorted cell strains, sorted CD146+/ALP−, CD146+/ALP+, and CD146−/ALP+ total collagenase-released cells (bar graph is representative of one of at least three independent experiments, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with CD146+/ALP− cells) were plated at clonal density and induced to myogenic differentiation (2% horse serum on Matrigel), high numbers of myotubes expressing skeletal muscle-specific myosin heavy chain (MyHC, red) are found in freshly sorted cultures enriched in MU CD146+/ALP− cells. Only rare myotubes are observed in cultures of CD146+/ALP+ cells. Scale bar represents 120 μm.
(D) Immunolocalization analysis of the distribution of CD146 and ALP expression in intact muscle revealed that while ALP cells (green, arrow, upper left) were predominantly expressed in precapillary arterioles, CD146 cells (red, arrows, center and lower right) were predominantly expressed in large venules (v). Scale bars represent 100 μm or 120 μm as indicated.
(E) A subset of vascular-wall-associated cells was found to express PAX3 (red, left panel) and PAX7 (red, right panel) in intact adult skeletal MU. Immunoreactivity was distributed to the surface of myofibers (MF) in a satellite cell-like position (arrowhead) underneath the basement member (laminin, green), and to BV walls (V). Scale bars represent 10 μm or 25 μm as indicated.
(F) Freshly isolated, uncultured CD146+ cells were found to co-express the satellite cell marker, PAX7.
All data shown are representative results from one of at least three independent experiments.