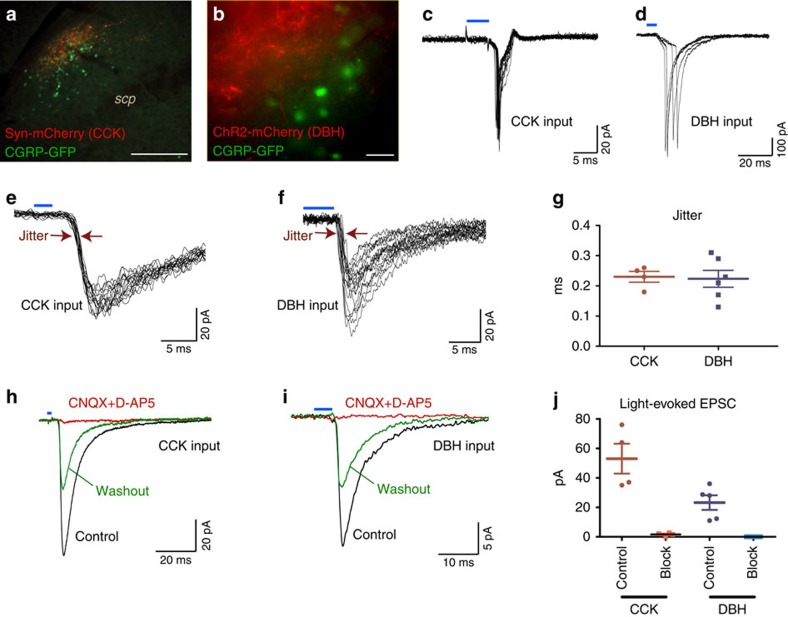
Figure 5. CCKNTS and DBHNTS neurons send direct, excitatory input to CGRPPBN neurons.
(a) Representative immunohistological image from the PBN showing CCK fibre terminals in red and CGRP-expressing cell nuclei in green after injecting AAV1-DIO-synaptophysin:mCherry into the NTS of a CckCre/+::CalcaCre:GFP/+ mouse. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Live imaging of the lateral PBN before electrophysiological recording in a DbhCre/+::CalcaCre:GFP/+ mouse. Red fibres, from DBHNTS neurons targeted for photostimulation and green nuclei indicate CGRPPBN neurons targeted for recording. Scale bar 20 μm. (c,d) Action potentials recorded in cell-attached configuration and evoked in CGRPPBN neurons by stimulation of CCKNTS (c) and DBHNTS (d) axons by pulses of blue light indicated by blue bars. (e,f) Synaptic currents in CGRPPBN neurons following stimulation of CCKNTS (e) and DBHNTS (f) inputs by pulses of blue light indicated by blue bars. (g) Individual jitter values for synaptic currents in CGRPPBN neurons represented in e and f. (h,i) Representative traces from synaptic currents in CGRPPBN neurons, following stimulation of CCKNTS (h) and DBHNTS (i) inputs were reversibly inhibited by 20 μM CNQX and 100 μM D-AP5. (j) Quantitative effect of 20 μM CNQX and 100 μM D-AP5 (block) on synaptic currents represented in h,i. All currents were recorded in the presence of 100 μM picrotoxin.