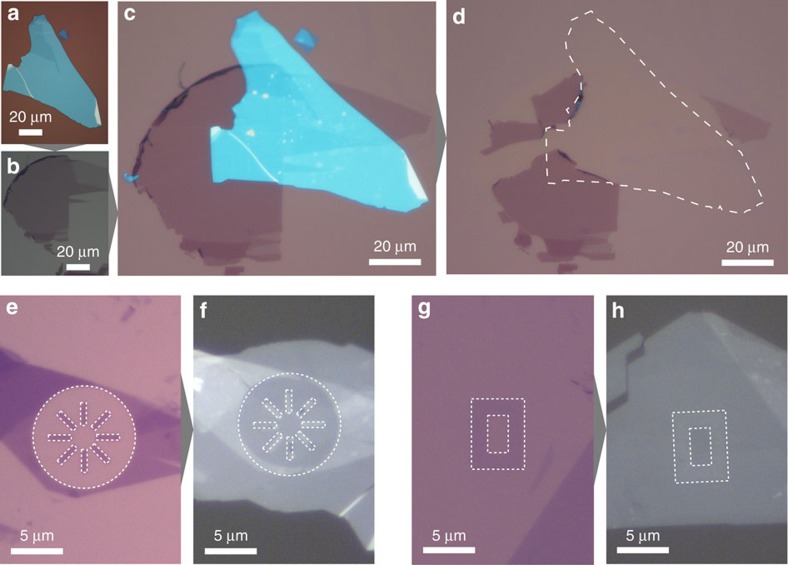
Figure 2. Adhesion between pristine and patterned 2D materials.
(a) hBN flakes are dropped down onto (b) graphene flakes (single and bilayer shown) to produce (c) a stack. (d) Interlayer adhesion between the hBN and graphene is sufficient to selectively tear the graphene away from the substrate. The dashed line indicates the previous extent of the hBN flake before pick-up. (e) A graphene monolayer which has been pre-patterned into eight rectangles (dark areas inside dashed lines) with EBL. (f) The graphene strips have been picked up by a hBN crystal and dropped down. The graphene is now the bright areas inside the dashed lines. Panels g,h same as e,f with a rectangular graphene frame. This approach allows multiple stacking of laterally patterned two-dimensional layers into complex three-dimensional heterostructures.