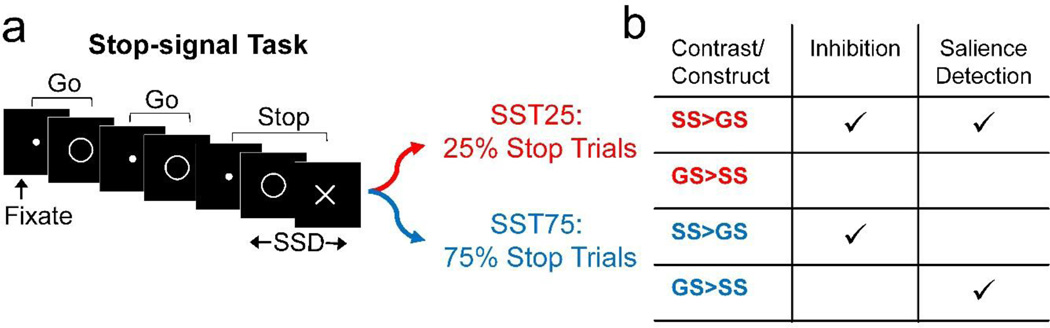
Figure 1.
a) Stop-signal task (SST) design. All participants performed two versions of the task: SST25 (25% stop trials) and SST75 (75% stop trials). b) The contrast SS > GS measures both response inhibition and salience detection in SST25, but only inhibition in SST75, where stop trials predominate. SS = stop success, GS = go success, SSD = stop-signal delay. A conjunction of SS > GS between SST25 and SST75 identifies correlates of “stopping,” whereas a conjunction of SS > GS in SST25 and GS > SS in SST75 identifies correlates of saliency detection.