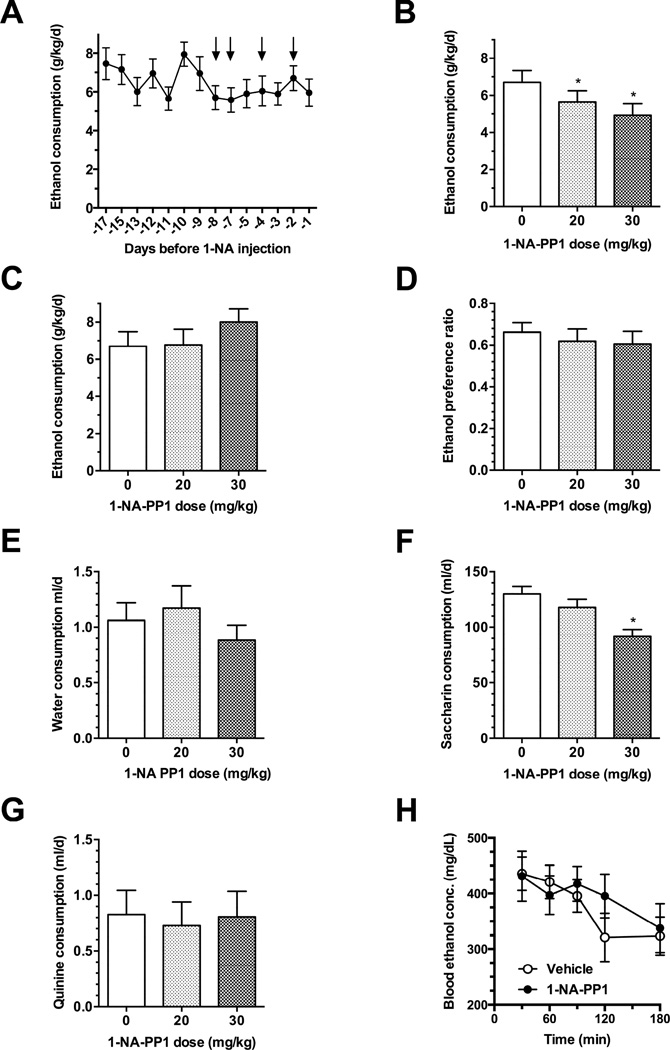
Fig. 4.
Ethanol consumption by AS-PKCε mice. (A) AS-PKCε mice were habituated to vehicle injections and allowed to achieve a stable baseline level of drinking. Arrows point to days when animals received vehicle injections. 1-NA-PP1 reduced ethanol consumption (B) and this effect was reversible since it was no longer present 48 hours after administration of 1-NA-PP1 (C). (D) 1-NA-PP1 did not alter preference for ethanol over water or water intake (E) 1-NA-PP1 (30 mg/kg) reduced saccharin intake (F), but not quinine (G) intake.(H) 1-NA-PP1 (30 mg/kg) did not alter ethanol clearance. *P < 0.05, Dunnett’s test; n = 18 per group (A-E), n = 14 per group (F and G), n = 7 per group (H).