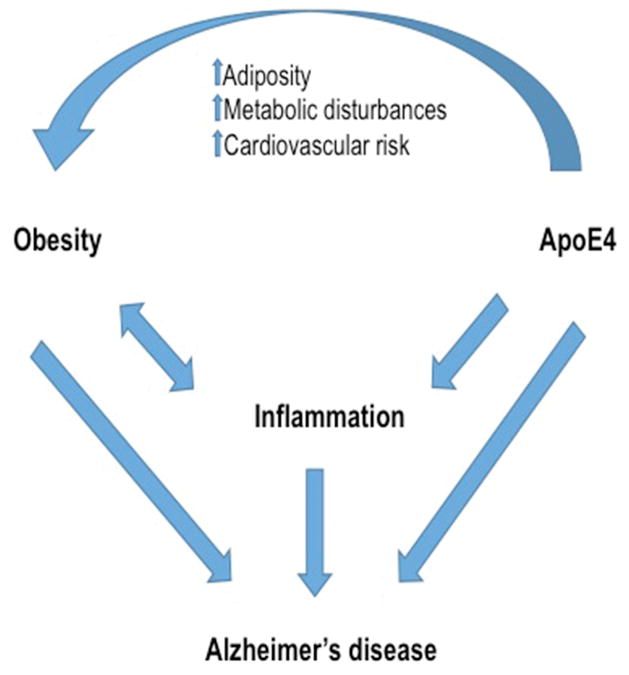
Figure 1. Interactions between obesity, apoE4 and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk and pathology are increased by a number of factors and pathways, many of which interact with each other. As diagrammed here and described in the text, apoE4 and obesity independently increase AD risk as well as inflammation, which also contributes to AD risk. Moreover, apoE4 carriers have been shown to be more at risk for a number of obesity-related complications, including increased adiposity, metabolic disturbances, and cardiovascular risk. Thus, apoE4 and obesity appear to both independently and cooperatively increase inflammation and AD risk.