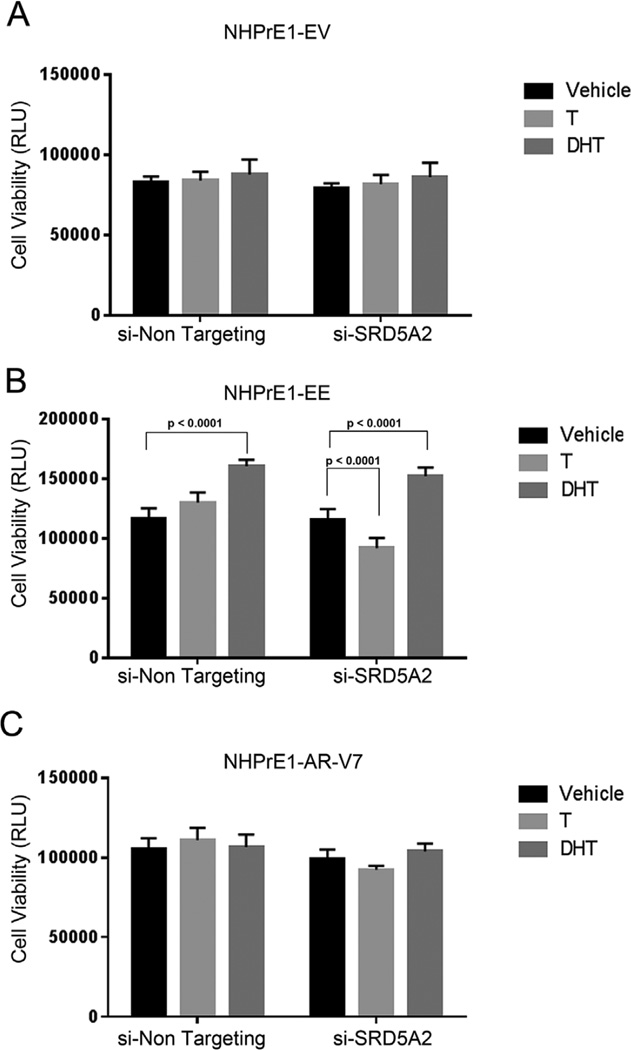
Fig. 5.
Knock-down of SRD5A2 decreased viability in cells with activated NF-κB. NHPrE1-EV (empty vector control— A) -EE (constitutively active NF-κB—B), and -AR-V7 (expressing AR-V7—C) cell lines were transfected with siRNA corresponding to SRD5A2 (si-SRD5A2) or a control siRNA (si-Non Targeting) and incubated in the presence of vehicle (Ethanol), testosterone 10−9 M (T) or dihydrotestosterone 10−7 M (DHT). Cell viability was examined over a three day period. (A) Suppression of SRD5A2 had no effect on NHPrE1-EV viability in the presence or absence of androgens. (B) The control (si-Non Targeting) NHPrE1-EE cell line responded to T and DHT and showed a significant (P < 0.0001) increase in viability in the presence of DHT. Knock-down of SRD5A2 resulted in a significant (P < 0.0001) decrease in cell viability even the presence of T but no change in the effects of DHT when compared to control cells. (C) NHPrE1-AR-V7 cells line had no change in viability when SRD5A2 was knocked down even in the presence of androgens. All experiments were performed three times with triplicate repetitions (n = 9). Bars are presented as standard deviation, P-value: two-way ANOVA.