Fig. 1.
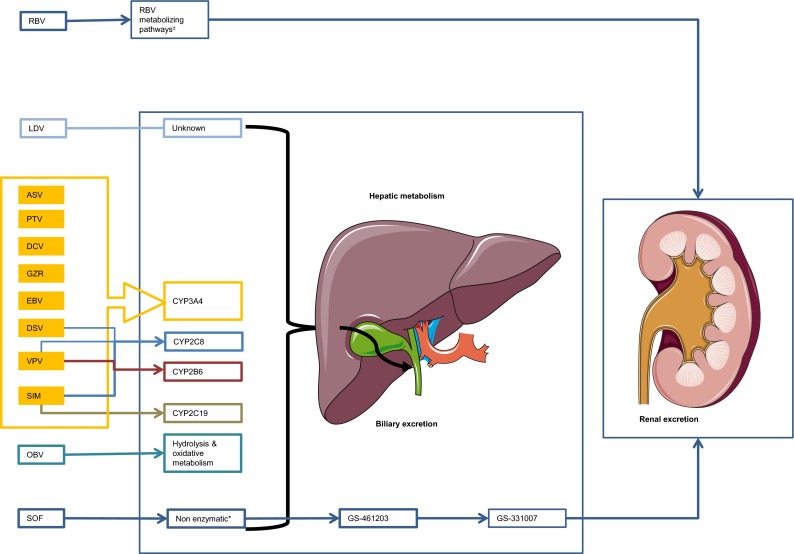
Overview of the hepatic or non-enzymatic metabolism of drugs used for the treatment of hepatitis C: cytochrome P450 enzymes involved and biliary and/or renal excretion of drug (metabolites). Asterisk The site of metabolism is unknown but two metabolizing pathways are involved: (1) a reversible phosphorylation pathway; and (2) a degradative pathway involving deribosylation and amide hydrolysis. Plus or minus Sofosbuvir is extensively metabolized in the liver in the active metabolite GS-461203, followed by dephosphorylation which results in the inactive compound GS-331007. ASV asunaprevir, CYP cytochrome P450, DCV daclatasvir, DSV dasabuvir, EBV elbasvir, GRZ grazoprevir, LDV ledipasvir, OBV ombitasvir, PTV paritaprevir, RBV ribavirin, SIM simeprevir, SOF sofosbuvir, VPV velpatasvir
