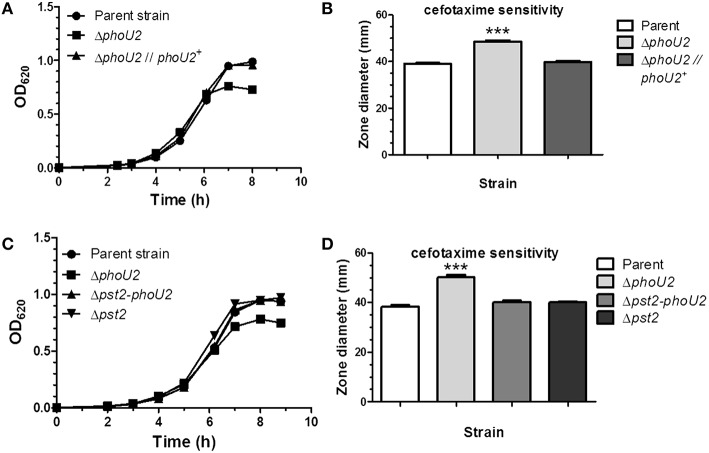
Figure 2.
Deletion of phoU2 leads to a lower growth yield and increased β-lactam antibiotic sensitivity that are reversed by a Δpst2 mutation. (A) Representative growth curves in BHI broth (≈18 mM Pi) of encapsulated parent strain (IU1781), a ΔphoU2 mutant (IU6375), and a ΔphoU2 mutant complemented by ectopic expression of PhoU2+ (IU6397). Strains were grown as described in Materials and Methods. A linear scale for OD620 is used to emphasize differences in growth yields. Growth yields and rates are quantitated for multiple determinations in Table S4. (B) Cefotaxime sensitivity assays of encapsulated parent strain (IU1781), a ΔphoU2 mutant (IU6375), and a PhoU2+-complemented ΔphoU2 mutant (IU6397). Cefotaxime disk sensitivity assays of bacteria grown in BHI broth were performed as described in Material and Methods. P-values were calculated by unpaired t-tests relative to the parent strain using GraphPad Prism; (n ≥ 3); ***P < 0.001. Increased sensitivity to other β-lactam antibiotics, vancomycin, gentamicin, and tetracycline of a ΔphoU2 mutant compared to its isogenic parent strain is shown in Table S5. (C) Representative growth curves of encapsulated parent strain (IU1781) and ΔphoU2 (IU6375), Δpst2-phoU2 (IU6550), and Δpst2 (IU6610) mutants in BHI broth. (D) Cefotaxime sensitivity assays for encapsulated parent strain (IU1781), and ΔphoU2 (IU6375), Δpst2-phoU2 (IU6550), and Δpst2 (IU6610) mutants. (n ≥ 3); ***P < 0.001.