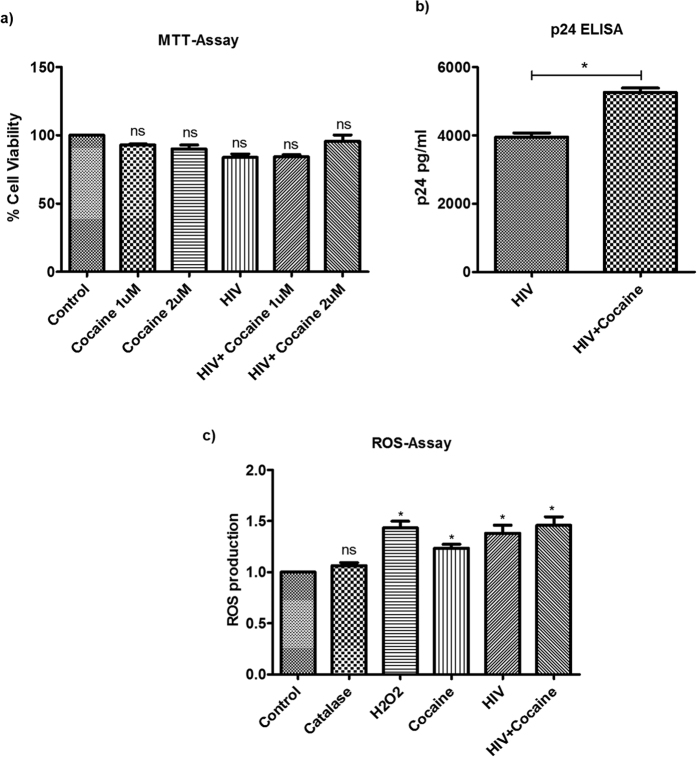
Figure 2.
(a) MTT Assay. Monocyte derived macrophages were infected with HIV and/or treated with cocaine for 10 days and the cell viability was measured using the MTT assay. We have found no significant cytotoxicity in the macrophages at the concentration of cocaine or HIV used in the study. (NS-Not Significant). (b) Increased HIV infectivity of MDMs in the presence of cocaine. Monocyte derived macrophages were infected with HIV in the presence/absence of cocaine for 10 days and the HIV infectivity was measured by measuring the p24 antigen production in the culture supernatant using the p24 antigen ELISA Kit. We have found significantly increased HIV infectivity in macrophages exposed to cocaine than the HIV infected cells alone. (*p ≤ 0.05). (c) ROS Assay. Monocyte derived macrophages were infected with HIV and/or treated with cocaine for 10 days and oxidative stress was analyzed by ROS assay. We have found significant ROS production in cocaine alone treated, HIV only infected and HIV plus cocaine treated macrophages. (*p ≤ 0.05; NS-Not Significant).