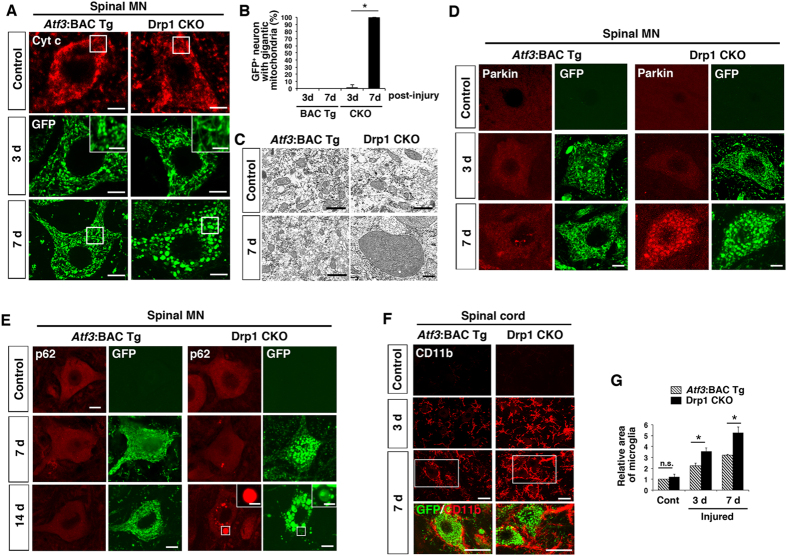
Figure 6. Injury-inducible Drp1-deficient motor neurons affect mitochondrial and neuronal integrity during first 7 days after injury.
(A) The immunohistochemical staining of mitochondria using Cyt c antibody for control motor neurons and GFP antibody for injured motor neurons. High magnification of mitochondria at 3 days after injury is shown in insets. The area surrounded by a box is magnified in (C). (B) The percent ratio of GFP-positive cells with spherical and gigantic mitochondria after nerve injury. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4 mice for each group, *p < 0.001). (C) Electron micrograph of mitochondria in motor neurons of Atf3:BAC Tg and Drp1 CKO mice using x 12,000 (excluding injured side of Drp1 CKO) and x 8,000 (injured side of Drp1 CKO) objectives. (D) Immunohistochemical staining of Parkin and GFP in spinal motor neurons of Atf3:BAC Tg and Drp1 CKO mice at control, 3 d and 7 d after sciatic nerve injury. (E) Immunostaining of p62/SQSTM1 and GFP in injured spinal motor neurons at control, 7 d and 14 d after sciatic nerve injury. Asterisk denotes mitochondrion magnified in inset. (F) Immunostaining of CD11b and GFP in injured lumbar spinal cord at 3 d and 7 d after sciatic nerve injury. The area surrounded by a white box is magnified in lowest panel. (G) Relative area occupied by microglia in injured spinal cord. Total area of microglial cells in 150 μm2 was quantified. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4 mice for each group, *p < 0.001). 3 d, 7 d and 14 d; 3, 7 and 14 days after nerve injury respectively. BAC Tg; Atf3:BAC Tg mice, CKO; Drp1 conditional knockout mice, Scale bars, 5 μm in (A), 3 μm (A and E, inset), 1 μm in (C), 10 μm in (D,E) and 30 μm in (F).