Figure 7.
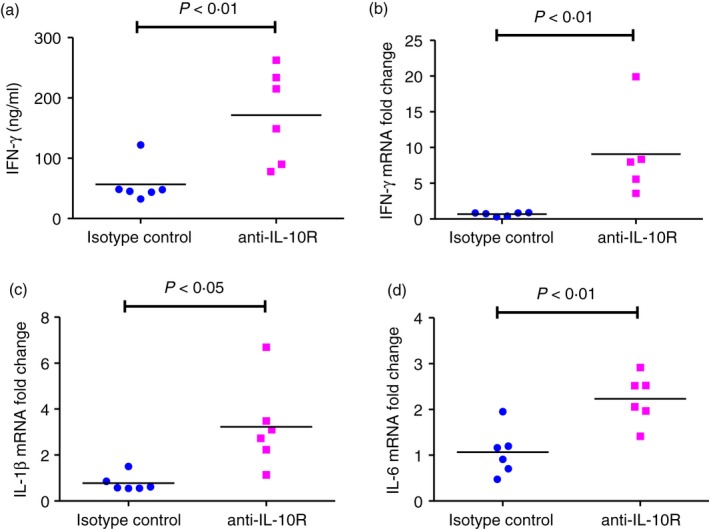
Interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ) production in 129SvEv wild‐type (WT) mice treated in vivo with anti‐interleukin‐10 (IL‐10) receptor specific antibody before and during Escherichia coli NC 101 monoassociation. Germ‐free (GF) 129SvEv WT mice were injected intraperitoneally with antibody that blocks the IL‐10 receptor (anti‐IL‐10R) or with isotype control antibody 1 day before, 2 days and 5 days after colonization with E. coli NC101. Mice were euthanized 7 days after monoassociation. (a) IFN‐γ production by unseparated mesenteric lymph node (MLN) cells stimulated in vitro with 10 μg/ml E. coli NC 101 lysate. Supernatants were collected 72 hr later and IFN‐γ was quantified by ELISA. (b) IFN‐γ mRNA expression, (c) IL‐1β mRNA expression, and (d) IL‐6 mRNA expression in transverse colon were determined by quantitative PCR. Copy number is normalized to GAPDH and expressed as fold change relative to isotype control. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data were analysed by unpaired Student's t‐test. P‐values indicate statistically significant differences between IFN‐γ for mice treated with isotype control antibody compared with mice treated with anti‐IL‐10R.
