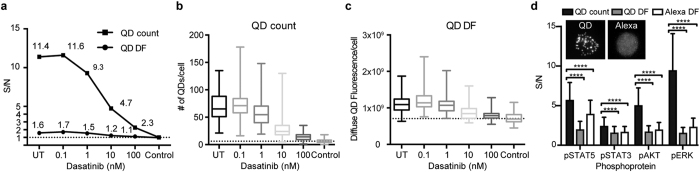
Figure 3. SC-QDP digitized counting sensitivity supersedes conventional summing of diffuse fluorescence in single cells.
(a) Plot of signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio for pCRKL quantification in K562 cells comparing the SC-QDP method of QD-nanoparticle counting (QD count) to QD diffuse fluorescence (QD DF) averaging in single cells, at increasing dasatinib concentrations. S/N is calculated by dividing the pCRKL level to that of the isotype control. UT is untreated cells. Dashed line is isotype control value. Numbers of cells sampled: 142, 159, 130, 117, 130, and 181 (left to right, x-axis). (b) Box plots showing the numbers of QDs/per cell in the SC-QDP from which S/N ratios were computed in Fig. 3a. Dashed line represents the noise which is the QD count for the isotype control. (c) Box plots showing the QD-DF per cell for a range of dasatinib concentrations. Dashed line represents the noise, which is the QD DF for the isotype control. Numbers of K562 cells sampled are same as given in panel a. (d) Single-cell phosphoquantification using the SC-QDP method of single cell QD-probe counting produces superior detection sensitivity compared to QD DF and Alexa DF per cell. Phosphoactivity levels (y-axis) computed in single untreated K562 cells for pSTAT5, pSTAT3, pERK, and pAKT. S/N ratio calculated by normalizing the phosphoactivity levels in untreated cells to the isotype control. Error bars are standard deviation. P values are calculated by the Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test, asterisks denote p value ≤0.0001. Inset shows representative images of pCRKL labeling by QD655 and Alexa 488 reporters in untreated K562 cells. The same primary phosphoantibody used for QD and Alexa labeling. Numbers of cells sampled are n = 637 (+/−169) for QD-labeling, and n = 940 (+/−118) for the Alexa 488- labeling.