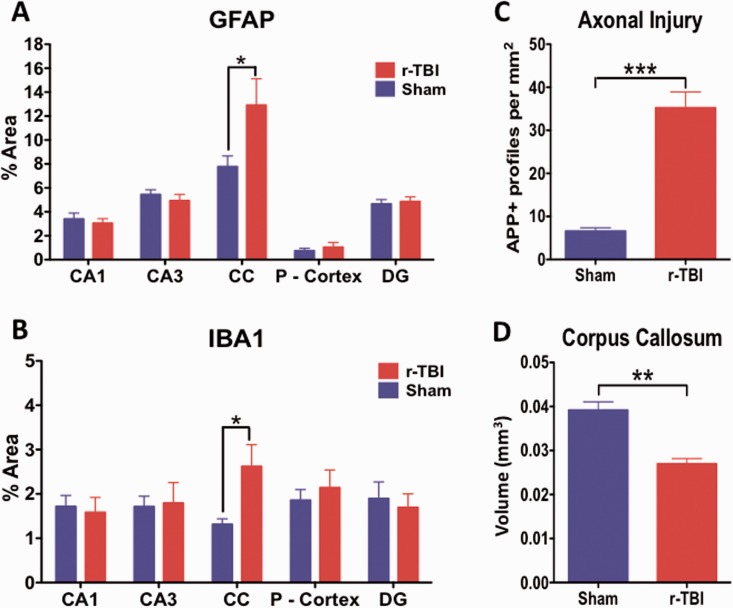
FIGURE 6.
Quantitative assessment of GFAP, Iba1, and APP immunostaining and corpus callosum volume in an hTau mouse model of chronic repeated traumatic brain injury (r-TBI). GFAP and Iba1 immunostaining are significantly upregulated in the corpus callosum of injured (r-TBI) vs. sham animals (A, B). No changes in GFAP or Iba1 were observed in other regions (gray matter) analyzed (A, B). (C) APP-positive spherical profiles in the corpus callosum were increased by ∼6-fold in the corpus callosum of injured versus sham animals. (D) The volume of the subregion of the corpus callosum bound by bregma (−0.36 to − 0.72 mm lateral) was significantly reduced by ∼30% in injured versus sham animals. N = 6 (sham/injured) for (A)–(C) and n = 4 (sham/injured) for (D); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. CC, corpus callosum; P-Cortex, parietal cortex; DG, dentate gyrus.