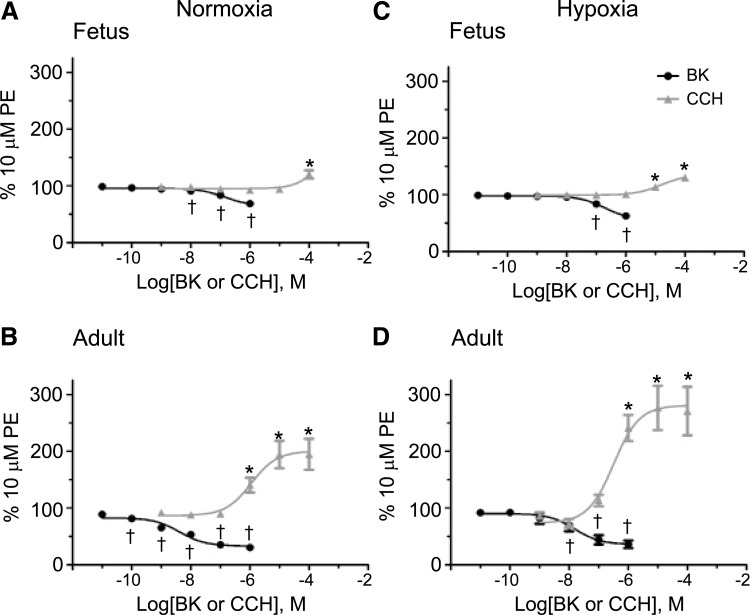
FIG. 2.
Maturation and chronic hypoxia modify bradykinin- and carbachol-induced pulmonary arterial reactivity. Dose–response curves of pulmonary arterial rings exposed to cumulative concentrations of 10 pM–1 μM bradykinin (BK) and 1 nM–100 μM carbachol (CCh) from normoxic fetuses (A) and adults (B) as well as chronic hypoxic fetuses (C) and adults (D). BK addition is documented by solid black circles and CCh addition by solid gray triangles. Lines show resultant fits with a Hill equation to the dose–response relationships and markers show mean ± SEM. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test analysis for each dose compared to control. Statistical significance is noted between bradykinin baseline (10 pM) and other concentrations (†p < 0.05) and between carbachol baseline (1 nM) and other concentrations (*p < 0.05).