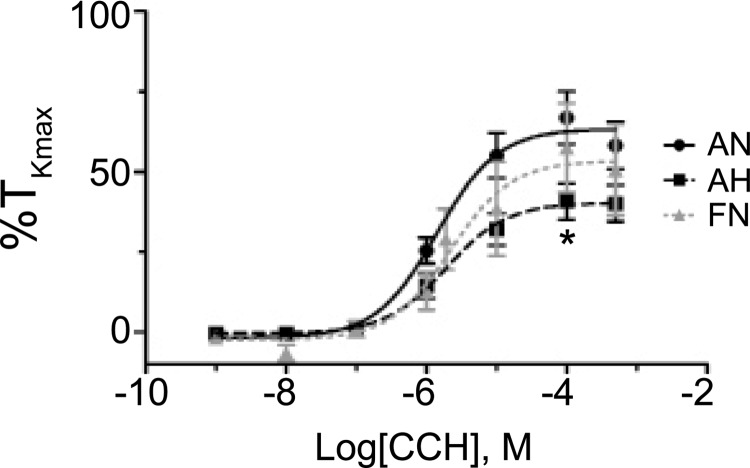
FIG. 4.
Chronic hypoxia decreases pulmonary arterial responsiveness to carbachol in adult sheep. Dose–response contraction curves of pulmonary arterial rings to 1 nm–100 μM carbachol (CCh) added in a cumulative manner normalized to %TKmax for adult normoxic (filled black circles, solid line), adult hypoxic (filled black squares, dashed line), and fetal normoxic (filled gray triangles, dashed line). Lines show resultant fits with a Hill equation to the dose–response relationships, and markers show mean ± SEM. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test analysis for each dose compared to control. Statistical significance is noted between adult normoxic and adult hypoxic groups (*p < 0.05). No differences were noted between the fetal and adult normoxic groups. Data were not generated for the fetal chronic hypoxic group because of the low percentage of responsive vessels. This figure and control traces for subsequent figures are based on 49 adult normoxic arteries (16 animals), 23 adult hypoxic arteries (7 animals), and 15 fetal normoxic arteries (11 animals).